First month for free!
Get started
Published 12/15/2025
At its core, an access control policy is just a set of rules that governs who gets to see and do what within your digital systems. Think of it as the bouncer for your company’s most sensitive information, deciding who gets in, where they can go, and what they’re allowed to touch.
These policies are the foundation of any serious security strategy.

Let's use a physical analogy. Imagine your company's digital assets—like customer lists, financial projections, or source code—are all stored inside a secure office building. Without a front desk or keycard system, anyone could wander in off the street, open any file cabinet, and walk out with your secrets.
That's where access control policies come in. They are that security system, but for the digital world.
This isn’t just some technical mumbo-jumbo for the IT team; it's a core business function. A well-crafted policy works like a modern keycard system. The CEO’s card might open every door, but a temporary contractor’s card only grants access to a single floor, and only between 9 AM and 5 PM on weekdays. It's all about granting the right access to the right people at the right time.
We used to think a strong firewall was enough, but in a world where internal threats are a major cause of data breaches, managing access inside the network is the real battle.
A solid access control strategy is critical for a few key reasons:
This proactive stance on security explains why businesses are investing so heavily in this area. The global access control market is expected to rocket from USD 19.05 billion in 2025 to USD 61.31 billion by 2035. You can dig into more data on the access control market growth to see just how quickly this is becoming a top priority.
Ultimately, mastering access control is not just about locking doors. It's about building a trusted environment where data is protected, productivity is enabled, and risk is intelligently managed.
Okay, so you're sold on the "why" of access control policies. The next big question is "how?" This is where you pick a framework—a blueprint for your digital gatekeeper—to make those critical access decisions.
There isn't a one-size-fits-all answer. The best model depends on your company's size, the complexity of your data, and your specific security goals. Let’s walk through the most common approaches.
The most popular and easiest-to-understand model is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). The concept is beautifully simple: permissions are tied to a person's job role, not to the individual.
Think about a hospital setting. The system assigns permissions based on roles like "Doctor," "Nurse," or "Billing Administrator." A doctor can view patient histories and write prescriptions. The billing admin can manage invoices but can't see sensitive clinical notes. When a new doctor joins, you just assign them the "Doctor" role, and they automatically get all the right permissions. It’s clean and efficient.
This straightforward approach is why RBAC is so common, especially in organizations where job functions are well-defined.
Here’s why it works so well:
But RBAC has its limits. It can be too rigid for complex situations. What if you need to restrict a doctor to only seeing patients on their assigned floor? That level of detail is where a more dynamic model shines.
For more fine-grained control, we have Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC). This model is a lot smarter and more aware of the context behind an access request. Instead of just looking at a job title, ABAC considers a whole range of attributes to make a decision in real time.
These attributes can be about anything—the user, the data, the device, or even the time of day.
For instance, an ABAC policy could say "grant access" only if all of these conditions are met:
This dynamic, rule-based approach is incredibly powerful. It allows you to build security logic that mirrors complex business rules, moving beyond static roles. A great example of this thinking in action is the Zero Trust Architecture, which operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify" for every single access request.
Ultimately, ABAC shifts the security mindset from "who you are" to "what you're doing right now." Access is continuously evaluated based on the full context of the request, making it a fantastic tool for enforcing sophisticated security policies.
So, which model is right for you? It really depends on your needs for simplicity versus granularity. This table breaks down the core differences to help you decide.
| Feature | Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Logic | Access is based on the user's assigned role (e.g., "Admin," "Editor"). | Access is based on policies that evaluate attributes of the user, resource, and environment. |
| Granularity | Coarse-grained. All users in a role get the same permissions. | Fine-grained. Policies can be extremely specific and context-aware. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible. Changing permissions requires changing role definitions. | Highly flexible. Policies can adapt to real-time contextual changes without altering roles. |
| Complexity | Simple to set up and manage, especially for smaller organizations. | More complex to design and implement due to the number of attributes and policies. |
| Best For | Organizations with clearly defined, static job functions. | Complex environments needing dynamic, context-aware security (e.g., IoT, big data). |
In the end, many organizations find that a hybrid approach works best—using RBAC for broad, role-based permissions and layering ABAC on top for situations that demand more specific, context-driven rules.
Every solid access control policy, no matter how simple or complex it looks on the surface, is pieced together from the same basic parts. Think of them as the LEGO bricks of your security system. Once you get a feel for how each brick works, you can build clear, effective rules that leave no room for guesswork.
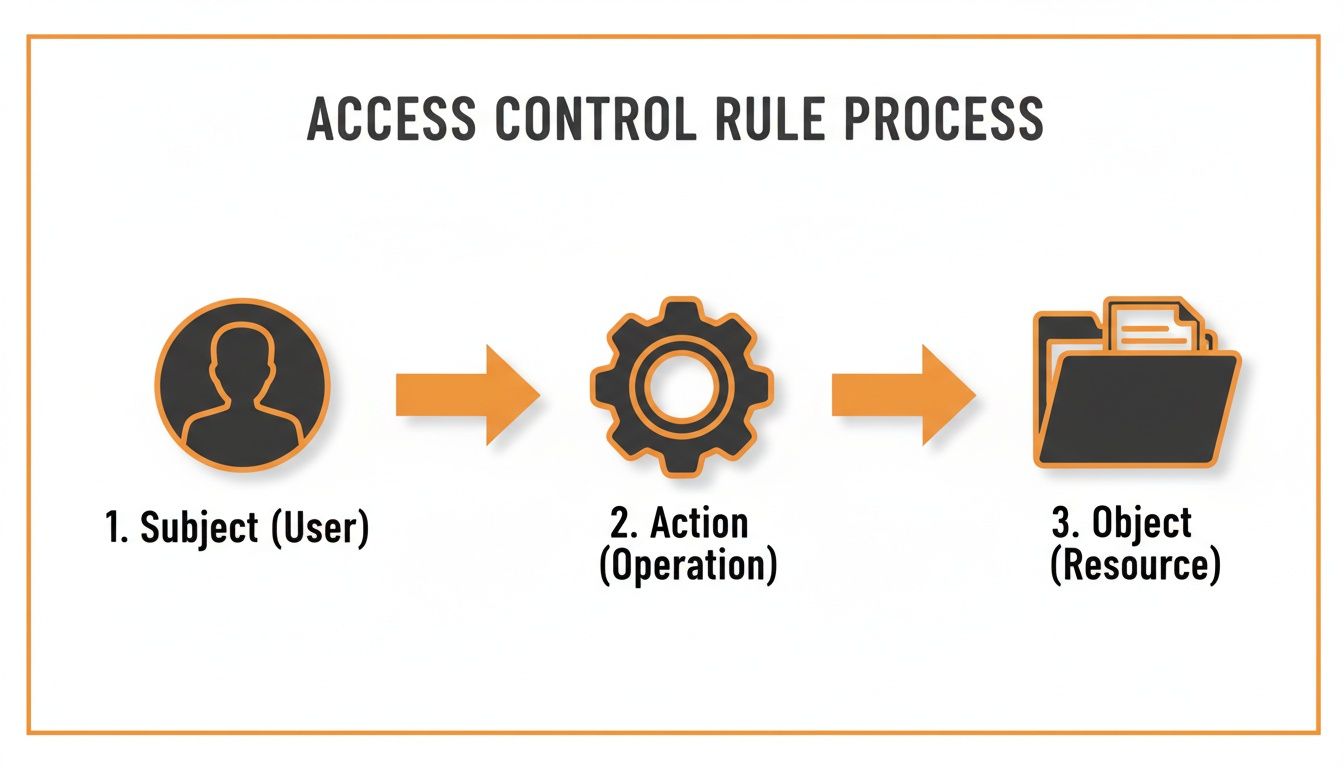
At the end of the day, every single access request comes down to one simple question: should this person be allowed to do this thing to that resource right now? The building blocks of a policy are all about giving a precise, automated answer to that question.
To start writing good policies, you first have to understand their anatomy. Each rule you create is made up of four key pieces that work together to grant or deny a specific permission.
These are the essential components:
Let’s see how these pieces come together with a quick example. Imagine Sarah, a marketing manager working from home, needs to look at the quarterly campaign budget spreadsheet.
Here’s the breakdown:
The moment Sarah clicks to open that spreadsheet, a component called the Policy Decision Point (PDP) springs into action. You can think of the PDP as a digital bouncer at the door of your data. It instantly checks her request against the rules you’ve set.
The PDP looks at who she is (the subject), what she wants (the object), what she’s trying to do (the action), and the surrounding circumstances (the conditions). If everything lines up perfectly with the policy, the PDP says, "Permit," and the file opens. But if any single part doesn't match—say, she tries to delete the file or access it at midnight—the PDP returns a "Deny." This whole check happens in a flash, but it’s the core of how your security rules are actually enforced.
Getting a firm grip on these four building blocks—subject, object, action, and condition—is the absolute first step. It's how you write access policies that are not just secure, but also logical and easy to manage down the road.
Building a solid access control system isn't something you set and forget. It’s an ongoing process, a living part of your security strategy that needs to evolve with your business. If you treat it like a continuous cycle, you can build a framework that not only protects you today but adapts to whatever comes next.
Think of it as a simple, repeatable four-stage lifecycle. Each step feeds into the next, creating a loop of planning, implementing, checking, and refining that keeps your access rules sharp and effective.
You can't protect what you don't understand. Before you write a single line of policy, you have to get a handle on what you're actually trying to secure. This means identifying your critical digital assets—everything from the customer database in production to the proprietary code in your git repository.
Get the right people in the room for this. Talk to department heads, project managers, and team leads. They know exactly what information is vital to their day-to-day work and the real-world impact if that data were exposed. Your goal here is to create a complete inventory of your assets, classifying them by how sensitive they are.
With a clear map of what needs protecting, you can start writing the rules. Your guiding light through this whole process should be the principle of least privilege. It's a simple but powerful idea: grant only the absolute minimum access required for someone (or something) to do their job. Nothing more.
This is where you define roles and attach permissions to them. For instance, a "Content Writer" role might get 'create' and 'edit' access to the company blog, but strictly 'read-only' access to performance analytics. Once you've defined these rules, you implement them in your systems, whether that’s through your identity provider, cloud IAM settings, or application code.
At its core, every access decision boils down to a simple question: should this subject be allowed to perform this action on this object?
This fundamental logic is what powers every single authorization check your system makes, constantly weighing requests against the policies you’ve put in place.
A policy on paper is useless if it isn't being enforced correctly. This stage is all about verification. You need to keep a close eye on access logs to spot anything that looks out of place—a developer trying to access finance records, a user logging in from a strange location, or a flurry of failed login attempts.
You should also schedule regular access reviews. This is where managers have to sign off on their team's permissions, confirming that everyone still needs the access they have. It’s the single best way to combat "privilege creep," a common problem where employees accumulate more and more access over time, long after they stop needing it.
Regular auditing transforms your access control policy from a static document into a dynamic, active defense mechanism. It's the difference between having a rulebook and having a security guard actively patrolling the premises.
Finally, we close the loop. Based on what you find during monitoring and auditing, it’s time to refine your policies. This isn't a sign of failure; it's a sign the system is working.
Maybe you need to revoke a former employee's access, create a new role for a new team, or tweak permissions for a new software tool. This ongoing maintenance is what keeps your security framework flexible and strong, ensuring your policies stay aligned with the realities of your business and ready for the next cycle.
The theory behind access control is great, but the real magic happens when you see these policies working in the wild. They aren't just abstract rules; they're the invisible guardrails that keep modern businesses running safely and efficiently, no matter the industry.
Let's ground this in a few stories from the real world.
Picture a bustling hospital. A doctor needs immediate access to a patient's entire medical history—test results, diagnoses, clinical notes—to make a critical decision. At the same time, someone in the billing department needs to see that patient's insurance details and address to file a claim.
This is where a solid access control policy shines. It ensures the doctor sees the complete medical chart while the billing specialist can only access the specific demographic and financial data they need to do their job. This isn't just a smart security measure; it’s a non-negotiable part of HIPAA compliance that protects patient privacy and prevents costly data leaks.
The policy is constantly making decisions in the background, checking the user’s role (“Doctor” vs. “Billing Specialist”) and what they’re trying to view (“Clinical Notes” vs. “Insurance Details”) to grant or deny access instantly.
Every industry, from healthcare to finance, relies on tailored policies to solve tangible business problems and mitigate real-world risks. These rules are the silent guardians of sensitive information.
Now, let's step into a bank. A teller is authorized to handle routine customer transactions, like cashing checks and processing deposits. But what happens when a customer asks to wire $10,000? An effective access control policy steps in and blocks it.
The system recognizes that the teller's role doesn't permit them to approve a transfer of that size. Instead, the policy automatically flags the request and requires a manager's approval to proceed. This rule might look at the user's role ("Teller"), the transaction amount (an attribute), and maybe even the time of day to catch suspicious activity. It's a prime example of how firms are leveraging biometrics for fraud prevention to add even more layers of security.
This kind of layered defense is becoming essential. In North America alone, the access control market is expected to reach an incredible USD 6.88 billion by 2035, a clear sign that security is top of mind for everyone. You can learn more about the growing access control market and its drivers.
Finally, think about a fast-moving tech startup. Its developers need to get into production servers to deploy code and fix bugs. But leaving the doors wide open 24/7 is a security nightmare waiting to happen.
This is the perfect spot for a just-in-time (JIT) access policy. Instead of permanent credentials, a developer requests temporary access to a specific server for a set amount of time. The policy checks their role and an approved task ticket, grants access on the spot, and—most importantly—revokes it automatically when the time is up.
It’s a brilliant way to apply the principle of least privilege without slowing developers down.
Diving into access control can stir up a few questions. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to give you a clearer picture of how these policies work in the real world.
It’s easy to mix these two up, but they handle two very different parts of security. Think of it like going to a concert.
Authentication is showing your ticket at the gate. The staff scans it to confirm you're a legitimate ticket holder and lets you in. You’ve just proven who you are—or at least, that you have the right credentials.
Authorization is what happens next. Your general admission ticket lets you onto the main floor, but it won’t get you backstage. For that, you’d need a special VIP pass. That pass dictates what you're allowed to do now that you're inside. Access control policies are the rulebook for authorization, defining what an already authenticated user can actually see and touch.
Access control policies aren't something you can set up once and walk away from. The best practice is to perform a full review at least once a year, but you should also treat them as living documents that need attention whenever your organization changes.
You’ll want to trigger a review when:
Regular check-ins are your best defense against privilege creep, a sneaky problem where users accumulate more access rights than their job requires over time. Staying on top of reviews keeps your security tight and ensures you’re always sticking to the principle of least privilege.
Absolutely. You don’t need a massive budget or a dedicated IT security team to get this right. Many of the cloud services and SaaS platforms you already use have powerful, user-friendly access controls built right in.
A small business can make a huge leap in security by just focusing on the fundamentals:
This approach scales beautifully. As your business grows, you can evolve these foundational rules into more sophisticated policies without having to start from scratch. Starting simple is always better than doing nothing.
The core idea is that strong security isn't just for large enterprises. By thoughtfully applying access control principles, businesses of any size can dramatically reduce their risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Effective access control is about smart planning, not just expensive tools.
Need to transcribe audio or add voice to your applications? Lemonfox.ai offers high-quality, affordable Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech APIs built for developers and businesses. Get started with 30 free hours and see how easy it is to integrate powerful voice technology into your projects. Check out our simple pricing and robust features at https://www.lemonfox.ai.