First month for free!
Get started
Published 9/23/2025

So, what exactly is real-time speech-to-text? Think of it as live, automatic transcription. It’s the magic of watching spoken words instantly appear as written text on a screen.
This is a world away from services that just transcribe a recording after the fact. We're talking about capturing a conversation, a lecture, or a phone call as it happens.
Picture a personal stenographer who can type at the speed of human speech, catching every single word the moment it's spoken. That’s pretty much what real-time speech-to-text technology does. It’s a digital interpreter, listening to a live audio stream and converting it into text with almost no delay.
This isn't just a neat party trick; it's the engine behind some of the most dynamic digital tools we use today. Unlike old-school transcription that deals with audio files after an event is over, real-time services work in the now, opening up entirely new ways to interact and make information accessible.
The ability to turn spoken words into text on the fly is a game-changer in a lot of areas. When you see what's being said appear on a screen in near-real-time, you're not just reading—you're breaking down communication barriers and making things incredibly efficient.
This is crucial for things like:
At its heart, real-time speech-to-text closes the gap between the spoken word and the digital world. It makes information accessible, searchable, and useful the very second it’s created.
Throughout this guide, we'll pull back the curtain on how this all works. It feels like magic, but it’s really about sophisticated AI models that listen, understand, and write with incredible speed and accuracy.
You can think of it as a super-fast, three-step relay race:
This entire process happens in the blink of an eye, creating a seamless stream from sound to text. We'll dig into all of it—tackling challenges like latency and accuracy, exploring some fascinating use cases, and even walking you through how to add this technology to your own projects with tools like the Lemonfox.ai API.
At its heart, real-time speech-to-text is a bit like having a lightning-fast stenographer living inside your computer. It listens to someone speak and almost instantly types out what they're saying. This isn't just a simple recording; it's a complex, multi-stage process where an AI takes messy, analog sound waves and turns them into clean, structured digital text.
It all starts with a microphone capturing audio—the speaker's voice, the hum of an air conditioner, a car horn outside. This raw audio is the starting point for a fascinating journey from sound to sentence.
Before the AI can make sense of the words, it has to clean up the recording. This initial step is called signal processing. The system’s job here is to isolate the human voice and filter out all the distracting background noise. Think of it like a sound engineer meticulously tweaking a live recording to make the vocals pop.
Next, the system gets into feature extraction. The AI dissects the cleaned-up sound waves into their most basic components, which we call phonemes. Phonemes are the tiny, distinct building blocks of speech. For instance, the word "cat" is made up of three phonemes: the "k" sound, the "æ" sound, and the "t" sound. The AI is trained to recognize these unique acoustic fingerprints to figure out what's being said.
This infographic breaks down the high-level flow from sound capture to final text.
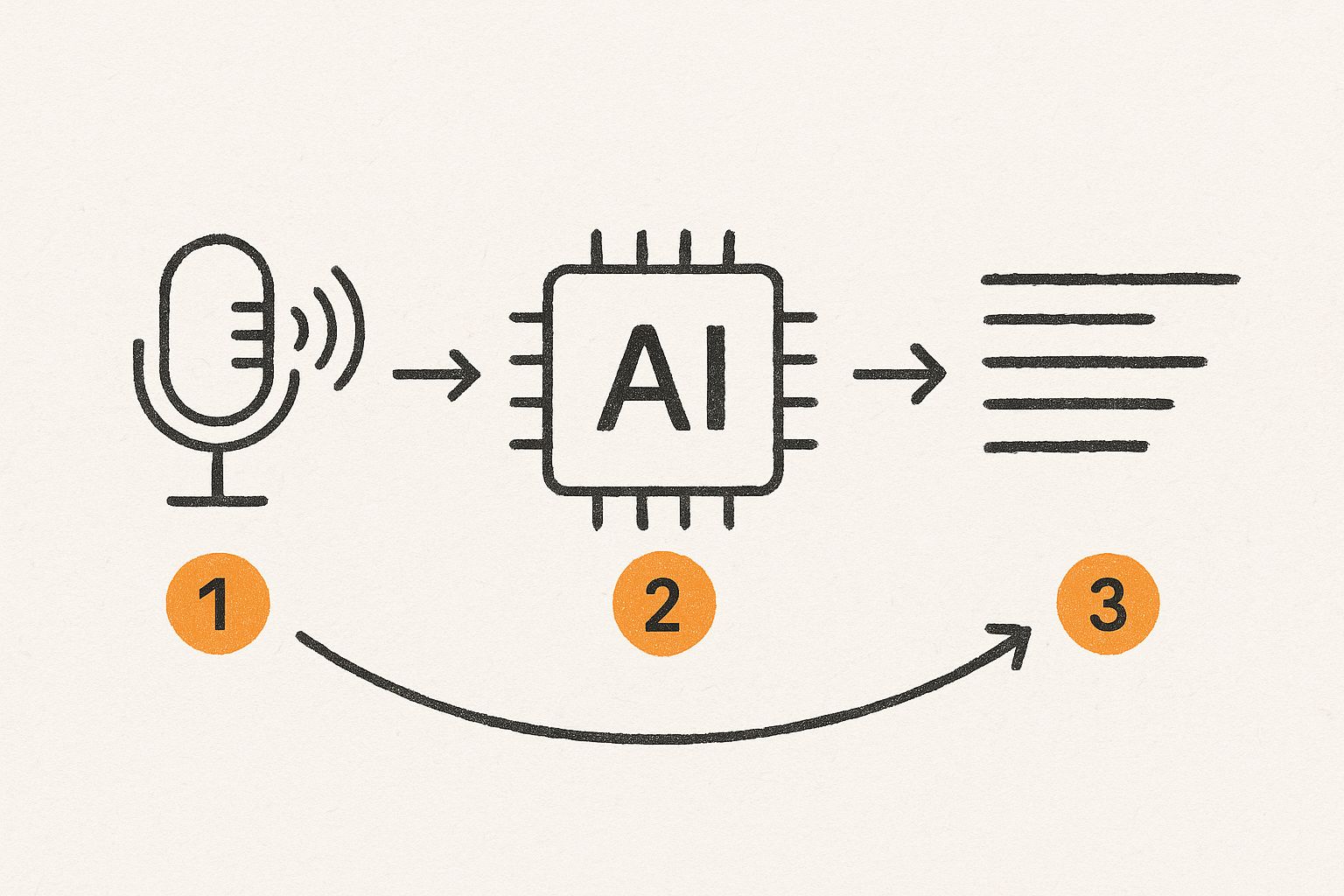
As you can see, it’s a direct pipeline: raw sound goes in one end, and after some specialized AI magic, readable text comes out the other.
With the audio broken down into its core components, the real heavy lifting begins. The system relies on two key AI models working together to decode what was said.
Acoustic Model: You can think of this as the AI’s phonetic ear. It's been trained on massive libraries of labeled audio to master the connection between acoustic patterns and specific phonemes. It essentially asks, "Given this sound I just heard, what is the most likely phoneme it represents?"
Language Model: This model is the brains of the operation, providing context and grammar. It looks at the sequence of phonemes and words to predict what the most probable sentence should be. This is how the system can tell the difference between "to," "too," and "two" or "their," "there," and "they're"—by understanding the words around them.
It's the seamless teamwork between these two models that makes accurate transcription possible. The acoustic model hears the sounds, and the language model helps put them together in a way that actually makes sense. Behind the scenes, this involves some pretty complex probability calculations to land on the most likely string of words.
This whole process—from capturing and processing the sound to decoding it into text—runs in a continuous loop. That’s what creates the "real-time" experience. Every component in the chain has to be incredibly fast to keep the delay between someone speaking and the text appearing on screen as short as possible.
For a deeper look into the different methods involved, this definitive guide on how to transcribe a conversation is a great resource, covering everything from manual techniques to the AI-driven approaches we've discussed.

While real time speech to text technology can feel like magic, making it seamless is a serious engineering challenge. Behind that fluid experience, developers are constantly wrestling with a few persistent problems that can make or break the whole thing. To get live transcription right, you have to conquer three major hurdles: latency, accuracy, and context.
It helps to think of it like a live television broadcast. Even a tiny delay is jarring, one misheard word can completely change a sentence's meaning, and without understanding the topic of the show, the captions might be nonsensical. For an AI, these problems are amplified, especially when you factor in the messy, unpredictable reality of human speech.
Getting past these obstacles is what separates a frustrating tool from one that's genuinely useful. So, let's break down each of these hurdles and look at the clever ways engineers are solving them.
In the world of live transcription, latency is the enemy. It's the technical term for the delay between someone speaking a word and you seeing it appear on the screen. For any real-time application, every millisecond matters. A system with high latency feels clunky and disconnected, making it impossible to have a natural conversation.
Just picture a customer service agent trying to use a live transcription to follow along with a caller. If the text is lagging a few seconds behind the audio, the agent can't respond in the moment. This leads to awkward silences and a terrible experience for everyone. The real goal is to make the transcription feel so immediate that it’s perfectly in sync with the speaker's voice.
The core challenge of latency is a balancing act. The AI needs enough audio to understand the context of a phrase, but it must process and display the text almost instantly to maintain a fluid, real-time feel.
Accuracy might be the most obvious challenge of them all. A system that constantly gets words wrong isn’t just unhelpful; it can be dangerously misleading. Getting this right is incredibly tough for a few key reasons:
To fight back, engineers use sophisticated noise-cancellation algorithms to clean up the audio before it even gets to the transcription model. They also build specialized models trained on industry-specific vocabularies, which can dramatically boost accuracy for professional use cases.
The final piece of the puzzle is context—the AI's ability to grasp the meaning behind the words, not just the sounds. Human language is full of ambiguity. Homophones, which are words that sound the same but have different meanings, are a classic example.
Take these three sentences:
An AI could easily get the word "right" wrong without understanding the rest of the conversation. This is where advanced Language Models (LMs) become so critical. By analyzing the entire sequence of words, the LM can figure out the most probable meaning, choosing the correct spelling and interpretation. This ability to resolve ambiguity is what makes a transcript not just accurate, but actually coherent and readable.
Getting all three of these elements—low latency, high accuracy, and contextual understanding—to work in harmony is the ultimate goal. The table below summarizes these common roadblocks and how modern systems are designed to overcome them.
| Challenge | Description | Common Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | The delay between when a word is spoken and when it's transcribed. High latency disrupts the flow of real-time interaction. | Streaming Architectures: Processing audio in small, continuous chunks rather than waiting for a full audio file. This allows for near-instantaneous output. |
| Accuracy | The system's ability to correctly identify words, especially in difficult conditions like noisy environments or with varied accents. | Advanced Noise Cancellation: Algorithms that filter out background noise. Also, training models on diverse datasets with multiple accents and dialects. |
| Context | The AI's struggle to understand homophones, slang, and industry-specific jargon, leading to nonsensical or incorrect transcripts. | Sophisticated Language Models (LMs): Analyzing surrounding words to infer the correct meaning and spelling. Also, using custom vocabularies for specific domains. |
As you can see, each problem requires a dedicated and clever technological approach. It's the combination of these solutions that powers the smooth, reliable real-time transcription experiences we're starting to see today.
The real magic of real time speech to text isn't just in the technology itself, but in how it’s being used to solve real-world problems. This isn't science fiction; it's a practical tool that's already overhauling workflows, boosting accessibility, and finding new efficiencies everywhere from chaotic hospital ERs to live global broadcasts.
The numbers tell the story. The global speech-to-text API market ballooned from roughly $1.32 billion in 2019 to around $3.81 billion today. That’s not just growth; it's a clear signal that businesses are seeing tangible value in turning spoken words into data.
Let's dig into a few areas where this technology is making a huge impact.
Doctors and nurses are drowning in administrative work. In fact, it’s not uncommon for physicians to spend hours every day just typing up notes and updating electronic health records (EHR). This isn't just inefficient; it's a major driver of burnout.
Real-time transcription provides a straightforward fix. Imagine a doctor having a natural conversation with a patient, and as they speak, their words are instantly and accurately captured in the EHR. This simple change allows them to focus entirely on the person in front of them, not the keyboard.
More importantly, it ensures crucial details are recorded on the spot, cutting down on the errors that can creep in with manual data entry hours later. For a deeper dive into this, you can find a lot more information on voice to text in medical settings and its benefits.
In the world of media and entertainment, real-time transcription is leveling the playing field. It's the engine behind live closed captioning for everything from the nightly news and major sporting events to your favorite streamer. This single capability means millions of people who are deaf or hard of hearing can be part of the conversation as it happens.
But it goes beyond accessibility. Media outlets can now create searchable archives of their live content almost instantly. A journalist can find a specific quote from a two-hour press conference in seconds, without having to scrub through the video. It makes every piece of live content more valuable and easier to reuse.
Real-time transcription closes communication gaps, making sure information isn't just captured in the moment, but is accessible to every single person.
In a call center, every second counts. Understanding a customer's issue right away is the difference between a great experience and a frustrating one. Real-time speech-to-text gives contact centers an incredible tool for analyzing calls as they happen.
As a customer explains their problem, their words are transcribed and analyzed for sentiment, keywords, and intent. This unlocks some powerful, immediate benefits:
This instant feedback helps agents solve problems on the first try—a huge win for customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. By turning spoken conversations into structured data, businesses get a much clearer picture of what their customers actually want and need.
Picking the right real time speech to text provider can feel like trying to find a needle in a haystack. There are dozens of APIs out there, and they all claim to be the best. The trick is to cut through the noise and focus on what actually matters for your project.
A solution that's perfect for live broadcast captioning might be a terrible choice for a medical dictation app. So, before you even start looking at providers, you need to map out what success looks like for you. This simple step—creating a checklist of your technical and business needs—will save you a world of headaches down the road.
Everyone talks about accuracy, but it's not some universal number. A provider might boast 95% accuracy on their website, but that figure was likely achieved with pristine, general-purpose audio. Throw in your industry's specific jargon, and that number can nosedive.
Think about it: a legal transcription tool has to nail words like "subpoena" and "exculpatory," while a medical tool needs to understand complex drug names without fail.
Before committing, you absolutely have to test any service with audio that reflects your actual use case. That means using your specific jargon, typical background noise, and the accents of your users. A free trial, like the one from Lemonfox.ai, is the perfect way to do this kind of real-world stress test.
This hands-on approach will give you a far more honest picture of performance than any marketing benchmark ever will.
When it comes to real-time applications, speed is everything. The gap between someone speaking and their words appearing as text has to be almost imperceptible for the experience to feel natural. High latency can make an AI voice assistant feel clumsy or cause live captions to lag hopelessly behind the conversation.
Don't be afraid to ask potential providers for their average latency numbers, and then test those claims yourself. A few hundred milliseconds can be the difference between a genuinely useful tool and a frustrating gimmick.
Basic transcription is just the start. The real magic often lies in the advanced features that can solve specific problems. Here are a few to look out for:
The demand for these kinds of sophisticated tools is exploding. In fact, the global speech-to-text API market is expected to grow from around USD 3.81 billion to nearly USD 8.57 billion by 2030. It’s a clear sign that voice-powered technology is becoming central to how we interact with software.
As you get started with real time speech to text, you’re bound to have some questions. We've gathered some of the most common ones here to clear things up, set the right expectations, and give you a few practical tips for getting great results.
It all comes down to timing. Batch transcription is a lot like dropping off film to be developed—you hand over a finished audio file and get the text back later. It’s the perfect solution for turning recorded interviews, meetings, or podcasts into text after the fact.
Real-time transcription, on the other hand, is like a live news ticker. It processes audio as it's being spoken, feeding you a continuous stream of text. That instant feedback is critical for things like live closed captions, voice-controlled apps, or analyzing a customer service call while it's still in progress. You simply can't wait for the recording to end.
This is the big question, and the honest answer is: it depends. In a perfect world—with a clear speaker, a high-quality microphone, and zero background noise—the best models can hit over 90% accuracy. But the real world is rarely perfect.
The only way to know for sure is to test a service with audio that mirrors your actual use case. Things like background chatter, people talking over each other, or strong accents are the ultimate stress test for any transcription system.
While the core AI model is out of your hands, you have a surprising amount of control over the final output. The secret is to feed the system the cleanest audio possible.
Here are a few things that make a huge difference:
Ultimately, by giving the real time speech to text model a clean signal to work with, you’re setting it up for success.
Ready to see how fast, accurate, and affordable transcription can be? With Lemonfox.ai, you can get started for less than $0.17 per hour. Try our Speech-to-Text API with a free trial today!