First month for free!
Get started
Published 9/30/2025
If you need to transcribe a video, the most efficient way is to first pull the audio from it and then run that audio file through a solid Speech-to-Text API. This is worlds faster and more scalable than trying to do it by hand—you can get back a fully timestamped text file in just a few minutes.
Let's be real: manually transcribing video is a painful, slow process that just doesn't work when you have more than a handful of files. If you're managing a large media archive, building out training content, or trying to make sense of user-generated videos, you need a solution that can keep up. An API gives you the speed and accuracy to handle video transcription at any scale.
This isn't just about getting a text file. It’s about turning spoken words into structured, searchable data. Instead of spending hours scrubbing through a video to find where someone mentioned a specific term, you can just run a quick text search. This completely changes how you can work with your content.
An API like Lemonfox.ai doesn't just dump a wall of text on you. It gives you rich data, including precise timestamps for every single word. As a developer, this is where things get interesting, because you can build some seriously powerful features on top of that.
And of course, one of the biggest wins here is accessibility. Providing accurate transcripts and captions is crucial for making your content available to everyone. It’s a point well-covered in discussions around AI auto-captioning for enhanced accessibility.
Modern APIs like Lemonfox.ai are built with a clean, developer-first mindset. The goal is to let you add powerful transcription to your app with as little code and fuss as possible.
Video is everywhere, and the need to automatically transcribe it is exploding. We're seeing the market for these services grow like crazy to keep up. In fact, the online audio and video transcription market is on track to hit approximately USD 2.5 billion by 2025, and it's projected to grow at a 15% Compound Annual Growth Rate through 2033. You can dig into the numbers in this market growth trend analysis.
When you integrate a transcription API, you're doing more than just converting audio to text—you're future-proofing your application. You're building a foundation that can handle the massive and ever-growing volume of video content, letting you tap into its full potential. Moving from manual work to an automated process is a must for any modern app that deals with media.

Before you write a single line of code to call an API, let's talk about the source file. From my experience, the quality of your audio is the single biggest factor that will make or break your transcription accuracy. Sending a heavily compressed, noisy MP3 to a speech-to-text engine is like asking it to pick out a conversation in the middle of a rock concert—it’s just not going to work well.
The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" couldn't be more relevant here. To properly transcribe a video, your first move should always be to pull out the audio track and save it in a high-fidelity format. This isn't an optional step; it's a must-do if you want a clean, reliable transcript from the get-go.
You might be tempted to use a common format like MP3 because it’s small and convenient. The problem is, MP3s and other "lossy" formats are designed to save space by permanently throwing away audio data that the human ear might not easily perceive. An AI model, however, is much more sensitive. Once that data is gone, it's gone forever, often leaving behind subtle artifacts that can trip up the transcription engine.
This is exactly why you need to stick with lossless formats like FLAC or WAV.
The bottom line is this: never feed the audio straight from a video file into a transcription API. Always extract it and convert it to a lossless format first. You’re giving the AI the cleanest possible data to analyze, which pays off big time in accuracy.
For anyone comfortable with the command line, FFmpeg is an indispensable tool. It’s a free, incredibly powerful utility that can convert just about any media file you throw at it. Turning an MP4 video into a high-quality FLAC audio file, for instance, is just a single command away. I’ve seen this one simple step improve transcription accuracy by several percentage points.
When choosing your audio format, it helps to understand the trade-offs. Not all formats are created equal, especially when an AI is your audience.
| Audio Format | Compression Type | Best For Transcription Accuracy? | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLAC | Lossless | Yes (Recommended) | Perfect quality with smaller file sizes than WAV. The ideal balance. |
| WAV | Uncompressed (Lossless) | Yes | The absolute best quality, but results in very large files. |
| MP3 | Lossy | No | Discards audio data, which can introduce errors and hurt accuracy. |
| AAC | Lossy | No | Similar to MP3, this format is designed for listening, not analysis. |
Ultimately, formats like FLAC and WAV preserve the original audio waveform perfectly, giving the transcription model all the information it needs. Lossy formats like MP3 and AAC compromise on data to save space, which is the exact opposite of what you want for a high-accuracy task.
Beyond just the file type, two other technical details really matter: sample rate and bit depth. The sample rate, in particular, has a direct impact on the quality of your transcript.
Think of the sample rate as the resolution of your audio. A low sample rate is like a blurry, pixelated photo, making it hard to distinguish details. A high sample rate gives the AI a crystal-clear "image" to work with, making it much easier to differentiate between similar-sounding words and phonemes.
For the best results when you transcribe a video, you should aim for a sample rate of at least 16,000 Hz (or 16 kHz). This is widely considered the standard for high-quality speech recognition. Dipping below this threshold means you're actively degrading the source data, and you can expect the API’s performance to suffer.
Alright, let's get to the fun part. You've got your audio file prepped and ready to go, and now it's time to turn that sound into text using the Lemonfox.ai API. The whole process is refreshingly straightforward, so you can get a transcription back and start working with it in no time.
First things first: authentication. Once you've signed up, you'll find your unique API key on your dashboard. Guard this key carefully—it's your access pass. Every request you send to the API needs this key included in the header, which is how Lemonfox.ai knows the request is coming from you.
To actually talk to the API, you'll need a way to make HTTP requests from your code. If you're using Python, the requests library is a fantastic choice; for Node.js, axios is the go-to for many developers. Your goal here is to send a POST request to the Lemonfox.ai transcription endpoint, packing your audio file into the request's body.
The journey from your audio file to a finished transcript is pretty simple. You upload the file, the API works its magic, and you get structured text back.
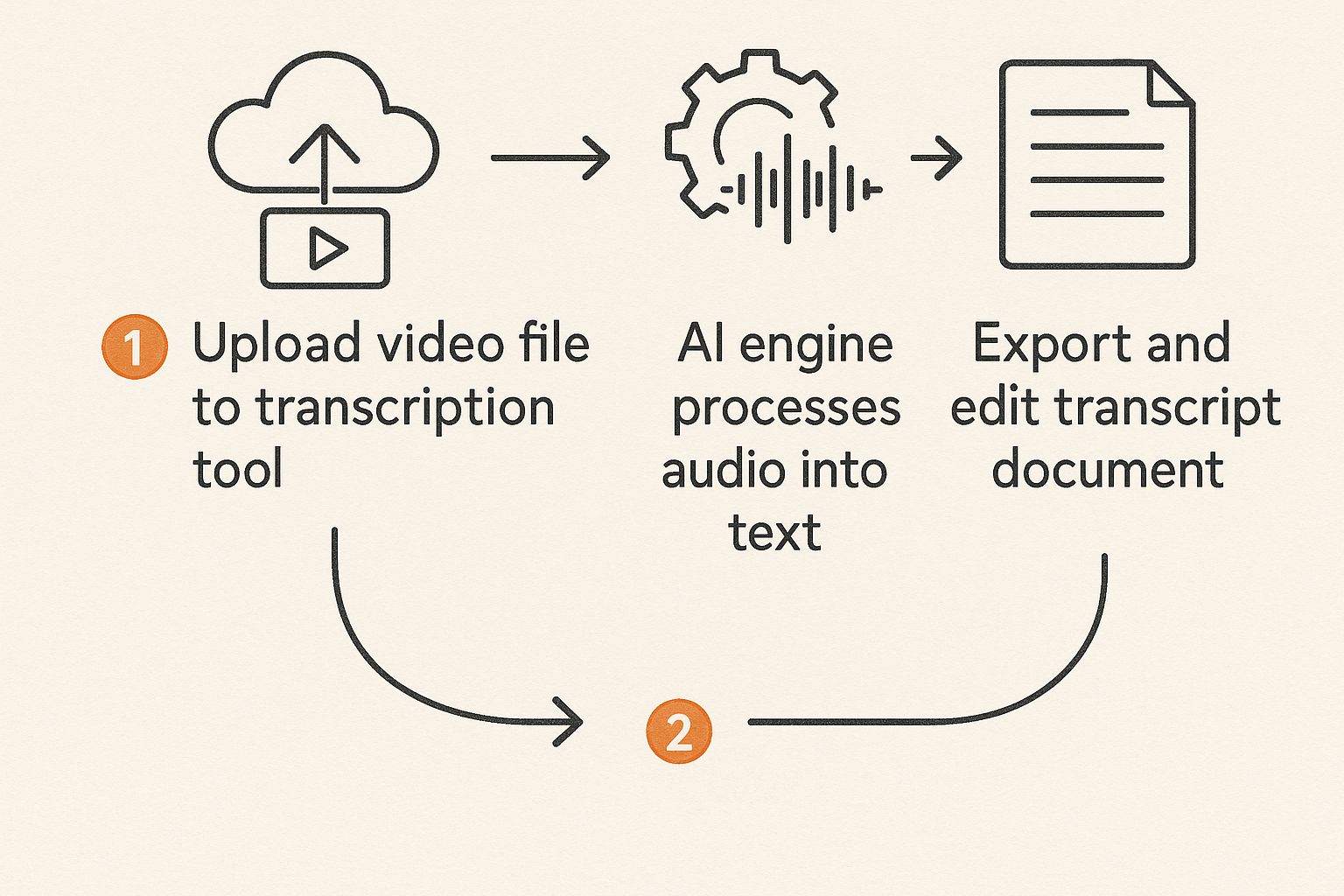
This graphic gives you a quick visual of the data flow, showing how the API acts as the engine for this whole conversion.
Here's a quick Python example to show you what this looks like in practice. This snippet opens your audio.flac file, sets up the authorization header with your API key, and sends it on its way.
import requests
api_key = "YOUR_LEMONFOX_API_KEY"
file_path = "path/to/your/audio.flac"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}"
}
with open(file_path, "rb") as audio_file:
response = requests.post(
"https://api.lemonfox.ai/v1/audio/transcriptions",
headers=headers,
files={"file": audio_file}
)
if response.status_code == 200:
transcription = response.json()
print(transcription['text'])
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")
print(response.text)
Think of this code as a solid starting point. When the API call is successful, it returns a JSON object, and you can easily pull out the full transcription from the text key.
While that basic call works perfectly for a simple transcript, Lemonfox.ai gives you more control with a few optional parameters. These are your tools for tailoring the output to exactly what you need.
language: You can give the API a hint by specifying the audio's language with its two-letter ISO-639-1 code (like 'en' for English or 'es' for Spanish). Lemonfox.ai is great at auto-detection, but telling it upfront can sometimes speed things up and improve accuracy.response_format: The default JSON is clean and simple. But if you need more detail, requesting verbose_json will give you word-level timestamps. This is a game-changer for building features like an interactive transcript player.diarize: Set this to true, and you'll enable speaker diarization. The API will analyze the audio and distinguish between different speakers, which is incredibly useful for transcribing interviews, podcasts, or team meetings.A truly useful transcription is more than just a block of text. It's about sending the right API request with the right parameters to get the data structured perfectly for your app—whether that's a simple transcript or a detailed script with timestamps and speaker labels.
The demand for this kind of detailed output is exploding. The U.S. transcription market hit an incredible USD 30.42 billion in 2024 and is on track to reach USD 41.93 billion by 2030. This isn't just a niche tool; it's a massive industry driven by the needs of media, healthcare, and legal fields that depend on accurate text. You can dive deeper into these numbers in this U.S. transcription market analysis.
Getting the raw transcript back from the Lemonfox.ai API is a great starting point, but the real power is in the details. The API’s JSON response isn’t just a simple block of text. It's a goldmine of structured data, packed with word-level timestamps that can turn a static transcript into a fully interactive experience for your users.
When you transcribe a video, this granular data is what separates a basic tool from a truly professional application. Let’s dive into how to unpack this output and put it to good use.
Once your transcription request is complete, the API sends back a JSON object. In its simplest form, you'll see a key like "text" which holds the complete, continuous transcript. For some quick and dirty jobs, that might be all you need.
But the real magic is tucked away in the verbose_json format. This detailed response organizes the entire transcript into segments, then breaks down each segment into individual words. And the best part? Every single word comes with its own start and end time. This is your raw material for building some seriously cool features.
Here’s what a single word object in the JSON looks like:
{
"word": "Hello",
"start": 0.52,
"end": 0.89,
"confidence": 0.98
}
This simple structure tells you everything: not just what was said, but precisely when it was said and how confident the model is about it.
Those start and end timestamps for each word are incredibly powerful. Instead of just slapping a wall of text next to your video, you can now link every word directly to its exact moment on the timeline. This unlocks a whole new level of user engagement.
Here are just a few ideas you can build out right away:
Features like these completely change the user experience, transforming passive viewing into an active exploration of your content.
The goal here is to move past a simple text dump. By parsing the timestamped data from the API, you are fundamentally changing how people can interact with and get value from your videos.
Let's say you're building a video player with a synchronized transcript sidebar. Using JavaScript, you can easily parse the JSON response and create HTML elements for each word. A common approach is to wrap each word in a <span> tag and add a custom data-start-time attribute.
It might look something like this in your HTML:
<span data-start-time="0.52">Hello</span> <span data-start-time="0.95">world</span>
From there, it's just a matter of adding a simple event listener. When a user clicks on one of these spans, your JavaScript can grab the start time from the data attribute and tell the video player to seek to that exact moment. It's a simple but incredibly effective technique, and it’s all made possible by the rich data the API provides.
A basic wall of text is fine, but it’s the advanced features that turn a raw AI transcription into a genuinely useful professional tool. This is where you can really elevate the final product for things like interviews, meetings, or panel discussions.
The most powerful feature, by far, is speaker diarization. This is the magic that automatically figures out who is talking and when. Instead of getting a single, confusing block of text, the API hands you a transcript that clearly attributes each line to the person who said it. If you're transcribing any video with more than one person, this is absolutely essential.
Once the API gives you the speaker labels, the next step is to put that data to work. A little bit of post-processing can format the transcript to look more like a movie script. You just need to loop through the text segments and add the correct speaker label—like "Speaker 1:" or "John Doe:"—before each one.
This one change makes the final document a thousand times more readable. Anyone can immediately see who said what and follow the natural flow of the conversation. Trying to make sense of a meeting or interview transcript without these labels is a nightmare.
A great transcript isn't just accurate; it's organized. Using speaker diarization to create a script-like format is the difference between providing raw data and delivering a truly valuable, easy-to-digest resource for your users.
This kind of organization is no longer a "nice-to-have." With the massive shift to remote work, the demand has exploded. The market for video conferencing transcribing was already valued at USD 0.806 billion in 2024 and is on track to hit USD 1.18 billion by 2033. It's a clear signal of just how critical this functionality is. You can learn more about the growth of the video conferencing transcribing market and what's driving it.
Identifying speakers is the biggest leap, but smart punctuation and paragraphing are what add that final layer of polish. Raw AI output can sometimes be a bit clumsy, leaving you with long, unbroken text that’s a chore to read.
Fortunately, you can implement a few simple rules in your code to clean this up:
[00:01:23] at the start of a speaker's turn is a common and effective approach.When you combine speaker diarization with these intelligent formatting rules, you’re delivering a much more sophisticated product. You’re not just giving people words; you're handing them a structured, polished, and ready-to-use document. That final touch is what makes a transcription tool feel truly professional.
When you first dive into using APIs to transcribe a video, a few questions always seem to come up. Getting straight answers to these can save you a ton of headaches and help you build a much more solid application right from the get-go. Let’s walk through some of the most common hurdles developers run into.
This is the big one, right? The truth is, modern AI transcription APIs like Lemonfox.ai can hit 95%+ accuracy on audio that’s clear and well-recorded. That level of quality makes them a fantastic, scalable choice for most jobs, whether you're creating captions or building out a searchable video library.
Now, for really high-stakes material—think legal depositions or medical records—it’s still smart to have a human give it a final look for that last ounce of perfection. But for almost everything else, AI delivers a mix of speed, cost, and quality that manual transcription just can't touch.
Trying to transcribe a video that's an hour long or more with a single, direct request is a recipe for disaster. These synchronous requests often time out, leaving you with nothing but a failed job. The right way to do this, and the industry standard, is by using an asynchronous endpoint.
The process is far more dependable for bigger files:
Shifting to an asynchronous approach isn't just a "nice-to-have." It's essential for building a resilient application that can handle real-world media files without breaking a sweat.
So, what do you do when your video is packed with industry jargon, unique product names, or a bunch of acronyms? This is where a custom vocabulary feature, sometimes called "word boosting," becomes incredibly useful. Many advanced APIs, including Lemonfox.ai, offer this.
You simply provide a list of these specific terms before you start the transcription. The AI model then gets a heads-up to listen for these words, which can seriously boost accuracy for specialized content. It's a game-changer for making sure the terms that matter most to your business come through perfectly. Of course, beyond APIs, many people also look into the best software for transcribing video, which can offer different features and workflows.
Ready to see how simple and affordable it can be to transcribe a video for your project? With Lemonfox.ai, you get a developer-first API that delivers high accuracy and advanced features like speaker recognition for less than $0.17 per hour. Start your free trial today and get 30 hours of transcription on us.