First month for free!
Get started
Published 1/6/2026

If you're looking to connect with a global audience, producing top-notch voice overs in Spanish isn't just a nice-to-have anymore—it’s a core part of your strategy. Thanks to modern Text-to-Speech (TTS) APIs, creating authentic, localized audio is no longer a massive drain on time and resources. This guide is your roadmap, walking you through everything from picking the perfect dialect to fine-tuning your API calls for those big, ambitious projects.
The appetite for Spanish-language audio content is absolutely booming, and it's a golden opportunity for businesses and developers ready to meet that demand. We're talking about a market of over 460 million native speakers—one of the largest and most active digital communities on the planet. This goes way beyond simple text translation. It’s about creating genuine connections through voice, whether it's in a podcast, an e-learning course, a video game, or your next app.
For anyone on the development side, the big hurdle has always been producing natural-sounding audio that can scale. Let's face it, traditional voice-over work is a grind. It’s slow, expensive, and filled with back-and-forth between studios and voice actors. That old model just doesn't work for projects that need quick updates or localization for different Spanish-speaking regions.
The numbers speak for themselves. The Spanish-language audio space exploded with a 75% increase in 2023 alone, fueled by listeners hungry for podcasts and audiobooks. There are now nearly 750 companies in this ecosystem, a massive leap from just 423 the year before. And the content? We've gone from less than 1,000 Spanish audiobooks and podcasts five years ago to over 100,000 podcasts and 25,000 audiobooks today. If you want to dive deeper, a recent report on Spanish audio market growth breaks it all down.
A modern TTS API is your solution to this puzzle. It cuts through the slow, expensive workflows of traditional voice-over production, letting you meet this incredible demand head-on.
Innovations in localization, like sophisticated video translation tools, are also adding fuel to this fire by making it easier to adapt visual content. By plugging a TTS API into your workflow, you can sidestep the old bottlenecks and start delivering the kind of localized, natural audio experiences that truly connect with millions of listeners.
Let’s be honest: picking a "Spanish" voice isn't good enough. If you’ve ever heard a voiceover that felt just a little… off, you know what I mean. A voice that resonates with someone in Madrid can sound completely foreign in Mexico City, and that disconnect can tank your credibility before you even get to your main point.
There are over 20 Spanish-speaking countries, and the linguistic diversity is staggering. Authenticity is what builds trust, and choosing the right dialect shows you’ve done your homework. It tells your audience that you see them and understand their culture. The differences in pronunciation, slang, and even the rhythm of the language between Castilian, Mexican, and Argentine Spanish are not subtle—they’re fundamental.
Think carefully about who you're trying to reach. Are you producing a formal corporate training video for a company with teams across Latin America? That calls for a very different voice than, say, a punchy social media ad for Gen Z shoppers in the US.
A neutral Latin American accent can be a safe bet for a wide audience, but don't underestimate the power of specificity. A regional accent can create a powerful, immediate connection. Before you commit, always, always test voice samples with a script that reflects your real content. A voice might sound fantastic reading a generic phrase, but how does it handle your brand's unique terminology or the specific emotional tone you need to convey?
This decision tree can help you map out your needs, whether you're creating a one-off audiobook or a real-time voice assistant that needs to feel alive and responsive.
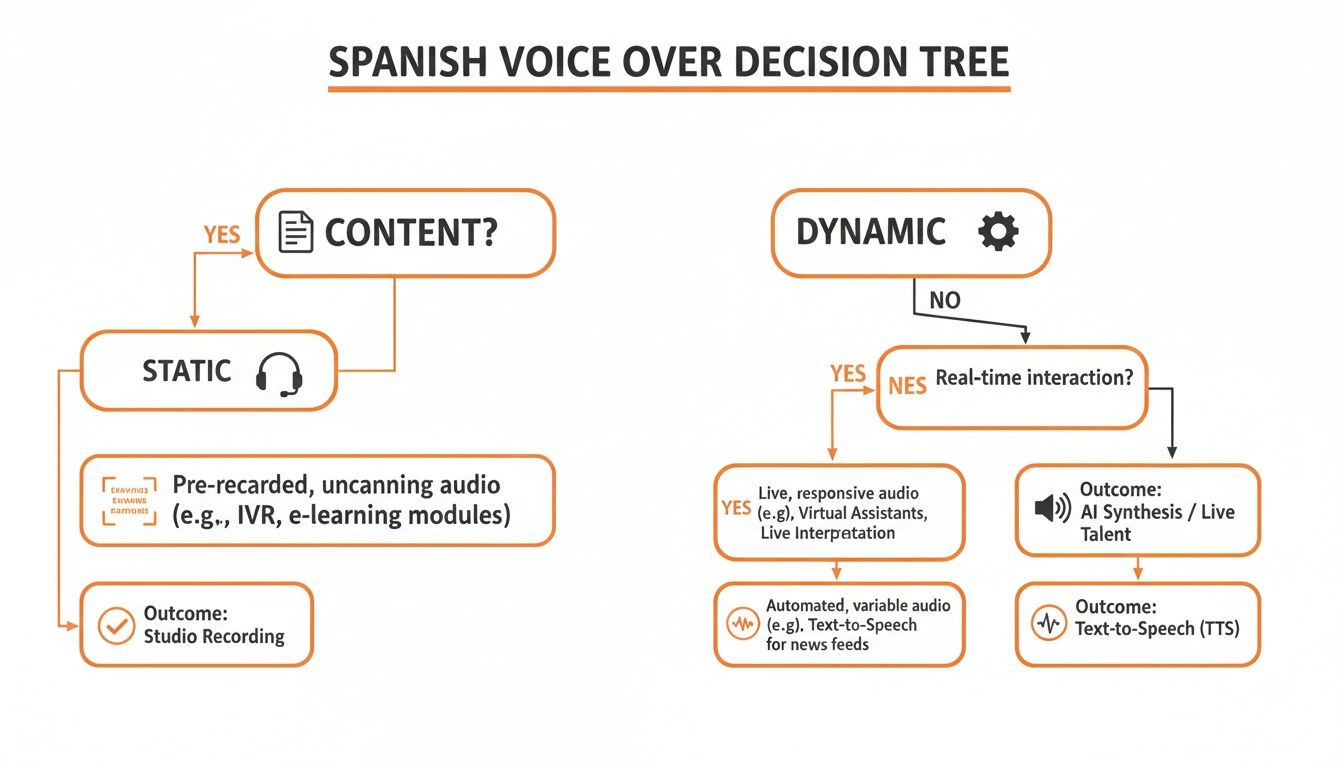
As you can see, the requirements for a static project are quite different from a dynamic application that demands constant updates or on-the-fly audio generation.
The numbers don't lie—getting this right is a huge opportunity. The global dubbing and voice-over market was already worth USD 2.89 billion in 2023 and is on track to hit USD 4.56 billion by 2032.
With over 460 million native speakers, Spanish is the second most spoken language on the planet, driving massive demand for localized content in everything from entertainment to advertising and e-learning. In fact, recent surveys show that 46% of businesses plan to prioritize Spanish voice-overs in 2025, just a hair behind English at 49%. You can dig deeper into these market trends and statistics to see just how critical localization has become.
Choosing the right dialect isn’t just a creative decision; it's a strategic one. It directly impacts engagement, comprehension, and how your brand is perceived in a specific market. Getting it right can be the difference between connecting with your audience and being ignored.
To help you get started, here's a practical breakdown of the most common dialects you'll encounter and where they shine.
| Dialect | Key Characteristics | Best For (Examples) | Lemonfox API Voice ID (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Castilian (Spain) | Distinct "th" sound for 'c' and 'z' (distinción). More formal intonation. | Corporate training for European teams, historical documentaries, luxury brand ads for the Spanish market. | es-ES-Standard-A |
| Mexican | Often perceived as clear and neutral. Widely understood due to media influence. | E-learning modules for a broad LATAM audience, animated content, neutral voice assistants. | es-MX-Standard-A |
| Rioplatense (Argentina/Uruguay) | Unique "sh" sound for 'y' and 'll' (sheísmo). Distinct, melodic Italian-like intonation. | Region-specific marketing campaigns, audiobooks by Argentine authors, localized travel guides. | es-AR-Standard-A |
| US Hispanic | A blend of influences, often with a neutral accent that avoids region-specific slang. | Public service announcements in the US, customer service IVRs, bilingual educational content. | es-US-Standard-A |
This table is just a starting point. The key is to listen, test, and align your choice with the specific expectations and cultural context of your target audience. Your users will thank you for it.

Getting a text-to-speech engine to just read your script is the easy part. The real art lies in making it sound like a person, not a machine. That's where Speech Synthesis Markup Language (SSML) comes in. Think of it as your director's toolkit for the AI voice actor, giving you fine-grained control to turn a flat reading into a genuinely expressive performance.
Your raw text is just the starting point. SSML is what lets you dial in the pacing, punch up the emphasis, and perfect the pronunciation. Instead of just taking the default output, you can actively shape the final audio to create high-quality voice overs in Spanish that actually connect with your audience.
This kind of control is no longer a nice-to-have. The market for AI-powered Spanish voice tech is exploding, hitting a value of USD 106.10 million in 2024 and on track to grow by 14.24% annually. As the platforms get better at handling different regional accents and emotions, your ability to master SSML is what will set your content apart.
One of the dead giveaways of a synthetic voice is its relentless, unnatural pacing. People pause. We take a breath, we let an idea land, we create suspense. The <break> tag is how you inject that natural rhythm into your audio.
Imagine you're building an e-learning module. You don't want to overwhelm the listener. A well-placed pause gives them a moment to process what they just heard.
Ahora, revisemos los resultados del primer trimestre. (Now, let's review the first quarter results.)<speak>Ahora, <break time="800ms"/> revisemos los resultados del primer trimestre.</speak>That simple 800-millisecond pause changes everything. It makes the delivery feel more intentional and authoritative. You can set these breaks in milliseconds (ms) or seconds (s), giving you surgical precision over the entire flow.
In any language, not all words are created equal. If you're writing a marketing script, your call to action needs to land with impact, not just be another part of the sentence. The <emphasis> tag is your go-to for making specific words or phrases stand out.
Let's say you're voicing an ad for a new app. The default reading might sound flat and uninspired.
Descarga la aplicación hoy y obtén un descuento especial. (Download the app today and get a special discount.)<speak>Descarga la aplicación <emphasis level="strong">hoy</emphasis> y obtén un descuento especial.</speak>By punching up the word "hoy" (today), you create urgency and excitement. It's no longer just a piece of information; it's a compelling invitation. A tiny tweak like this can make a huge difference in how your message is received.
SSML is the bridge between your script and a truly natural-sounding voice over. Mastering a few key tags gives you the power to direct the audio's pacing, tone, and clarity, elevating your project from good to exceptional.
TTS engines are incredibly smart, but they're not clairvoyant. They often stumble over brand names, industry jargon, acronyms, or foreign loanwords. A single mispronunciation can shatter the illusion and make your production sound amateurish. This is where the <phoneme> tag saves the day.
It lets you spell a word out phonetically using an alphabet like IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) or X-SAMPA, leaving nothing to chance. For instance, if your company is called "Solara" and the engine keeps mangling it, you can lock in the correct pronunciation for good.
<speak>Bienvenido a <phoneme alphabet="ipa" ph="soˈlaɾa">Solara</phoneme>.</speak>
This guarantees your brand name sounds right every single time, maintaining a professional and consistent audio identity. Of course, perfect pronunciation starts with a solid script. For a deeper dive into preparing your text, check out these excellent tips on converting video scripts for multi-language voiceovers.
Alright, let's move from planning to actually building something. This is where your chosen voice and carefully crafted SSML come to life. Making that first API call and hearing a perfect Spanish audio file come back is a great moment.
But going from a single successful test to a full-blown production environment requires a bit more strategic thinking, especially when it comes to performance and your budget. A simple, one-off approach is fine for a demo, but if you're building an app or service that people will actually use, you need a smarter, more efficient pipeline.
Your first real interaction with the API will likely be a simple POST request. You’ll send your text—wrapped in SSML, of course—along with the specific voice ID for your Spanish dialect and your preferred audio format.
Here's what that looks like in practice using JavaScript's fetch method. This snippet is a basic example of how to send a Spanish phrase to the API and get audio back.
async function generateSpanishVoiceover(text) {
const apiKey = 'YOUR_API_KEY';
const voiceId = 'es-MX-Standard-A'; // Example: Mexican Spanish voice
const apiUrl = 'https://api.lemonfox.ai/v1/audio/speech';
const response = await fetch(apiUrl, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Authorization': Bearer ${apiKey},
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
'model': 'lemon-fox-v1',
'voice': voiceId,
'input': text,
'response_format': 'mp3'
})
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(API request failed: ${response.statusText});
}
// Handle the audio stream or file
const audioBlob = await response.blob();
// ... code to play or save the audio
}
// Example usage
const script = "
generateSpanishVoiceover(script);
This request is the foundation for everything else you'll do. The real trick, though, is figuring out how to do this for thousands of sentences without slowing everything down or breaking the bank.
When you're working with a lot of content—like an e-learning module or an entire audiobook—sending a separate API request for every single paragraph is a recipe for disaster. It's slow, inefficient, and will quickly inflate your costs due to network latency and API call overhead.
The answer is batch processing.
Instead of tiny, individual calls, you group larger chunks of text into a single, more substantial request. For instance, combine a few paragraphs or even a whole chapter into one payload before sending it off.
Smart batching is a game-changer. By grouping text, you drastically reduce the number of API calls, minimize latency, and create a much smoother, more efficient generation workflow. This is essential for scaling any project involving voice overs in Spanish.
This strategy is especially powerful for static content that you can process all at once before your application even goes live.
Beyond batching, a few other techniques are crucial for building a cost-effective audio pipeline. Think of these as your go-to playbook for keeping your project financially viable as it scales.
Here are a few tactics I always rely on:
You’ve generated the audio, but you’re not quite at the finish line. The last mile is all about quality assurance (QA). This isn't just about spotting obvious mistakes; it's about ensuring your voice overs in Spanish sound polished, professional, and work perfectly no matter how someone is listening. Trust me, a tiny audio glitch can make an otherwise great project feel amateur.
First things first, listen for those classic text-to-speech artifacts. Your ears will pick them up if you listen closely—a slight metallic ring, a robotic cadence, or weird, unnatural pauses between words. I always pay extra attention to the pronunciation of localized terms, brand names, or any niche jargon. Even with your best SSML tuning, it’s a smart move to have a native Spanish speaker give any critical phrases a listen to make sure they land just right.
The real goal here is to make the technology invisible. Your audience should be completely absorbed in the message, not thrown off by a weird-sounding word or a technical hiccup.
The audio format you pick has a surprisingly big impact on everything from how fast your content loads to whether it even plays on certain devices. There's no one-size-fits-all answer here; the best choice really boils down to what you're building.
Here’s a practical look at the common options:
Anytime you send your text to a third-party API, you have to think about data privacy. It’s non-negotiable. Stick with providers who are upfront and clear about how they handle your data. You're looking for a firm commitment that they don't store your text or the audio they generate once the job is done.
This is especially critical if you have customers in the European Union. To stay on the right side of GDPR, using a service with an EU-based API endpoint is a must. For instance, a provider like Lemonfox.ai builds its service around privacy, deleting all data immediately after processing. This isn't just about checking a compliance box; it's about protecting your content and building trust with your users.
When you're plugging a new API into your stack, especially for something as nuanced as language, you're going to have questions. Getting ahead of the common roadblocks can save you hours of head-scratching and debugging later. Let's walk through some of the real-world questions that pop up when building voice overs in Spanish with a TTS API.
These aren't just hypotheticals—they're the practical hurdles you'll likely face when trying to localize content for millions of Spanish speakers.
This one comes up all the time. What happens with words containing the 'ñ' or accents, like in 'canción'? The good news is, any modern TTS API worth its salt is built to handle these perfectly.
The secret is to make sure your text is encoded as UTF-8 before you send it off in your API payload. UTF-8 is the web standard and it’s designed to support the full range of characters in Spanish. A quick check on your encoding prevents character corruption and ensures words like 'año' or 'niño' sound exactly as they should.
I always recommend running a quick test with a few tricky phrases. It’s a simple sanity check to confirm your setup is configured right and the API is hearing you correctly. It's a two-minute test that can prevent a lot of garbled audio down the line.
Absolutely, and it's not even close. Think about the traditional route: you're booking studio time, paying talent fees, and then paying again for any retakes or revisions. Those costs can easily spiral into hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars for a single project.
A TTS API completely changes the economics. You're typically paying for what you use—either by the character or the length of the audio generated. This pay-as-you-go model makes projects that were once financially impossible totally viable. For instance, you can now realistically:
For web applications, MP3 is almost always the right answer. It hits the sweet spot between decent audio quality and small file size. Your content loads quickly for users, and for spoken-word audio, there's no perceptible loss in clarity.
Sure, a format like WAV gives you uncompressed, high-fidelity sound, but the file sizes are massive and will bog down your site or app. OGG is another great open-source option with solid compression, but MP3 wins on universal support. It just works, everywhere, on every major browser and device. That reliability makes it the safest bet for delivering your voice overs in Spanish.
Ready to create scalable, natural-sounding Spanish voice overs without the traditional costs? Lemonfox.ai offers a powerful, privacy-focused Text-to-Speech API designed to make it easy. Explore the Lemonfox.ai API and start building your next audio experience.