First month for free!
Get started
Published 9/28/2025

When you hear "voice recognition software for healthcare," you're really talking about a smart tool that listens to a doctor-patient conversation and turns it into a perfectly organized clinical note. This tech lifts the massive weight of manual data entry off clinicians' shoulders, giving them back time to focus on what they're actually there for: taking care of people.
Think about your primary care doctor. After a full day of seeing patients, they're often stuck with another two hours of typing. Every symptom, diagnosis, and prescription has to be painstakingly logged into the Electronic Health Record (EHR). Clinicians even have a name for this dreaded after-hours work: "pajama time." It's a huge factor in burnout and it pulls focus away from patient care. This is exactly the problem that voice recognition software for healthcare was built to solve.
Now, imagine a different scenario. That same doctor is having a normal, back-and-forth conversation with a patient. In the background, an intelligent system is listening, picking out the medically important details, and dropping them into the right fields in the EHR as they speak. By the time the appointment is over, the clinical note is already 90% complete and waiting for a quick sign-off. This isn't science fiction; it’s what modern voice recognition does right now.
The first wave of this technology was pretty basic—just digital dictation. Doctors had to speak like robots, giving specific commands to get their words on the screen. Today’s tools are worlds away from that. They act more like a highly-trained assistant who understands the flow of a clinical visit.
Here’s what sets them apart:
This evolution from a simple transcription tool to a smart documentation partner is making a real difference in how care is delivered.
By automating one of the most draining parts of a clinician's job, this technology gets right to the heart of physician burnout. It frees up time and mental energy that can go straight back to the patient.
At its core, voice recognition software is the bridge between human conversation and the digital world of health records. It lets technology bend to the way doctors actually work, instead of forcing them to adapt to the stiff requirements of a keyboard. The result is more accurate records, faster documentation, and a much-needed return to patient-focused care.
Bringing voice recognition software into a clinical setting is about much more than just convenience—it fundamentally re-engineers the day-to-day rhythm of a healthcare facility. Think of it as creating a workflow where documentation happens almost invisibly in the background. This frees up clinicians to focus their complete attention on the patient in front of them.
This shift rests on three critical improvements: a major boost in efficiency, far greater accuracy in documentation, and a welcome reduction in physician burnout. Each of these pillars helps build a more resilient and patient-focused model of care.
The most immediate and obvious change is the jump in efficiency. Manual data entry is a well-known time drain, with doctors and nurses often spending hours every single day typing up notes, creating orders, and writing referrals. Voice recognition acts like a personal scribe, capturing information the moment it’s spoken and funneling it straight into the EHR.
This isn’t just about saving a few minutes here and there. For many physicians, this can return up to two hours per day to their schedule. That’s precious time they can reinvest in seeing more patients or, just as importantly, spending more quality time with the ones they have. This acceleration also ripples through the entire care cycle—when notes are done in real time, orders get placed faster, referrals are sent sooner, and billing is processed more quickly.
Beyond sheer speed, voice recognition software for healthcare brings a new level of precision to the table. Let’s face it, human error is part of manual typing, especially under the constant pressure of a packed clinic schedule. A single typo in a medication dosage or a misremembered detail from a patient’s history can have serious downstream effects.
AI-powered systems, on the other hand, are trained on enormous medical dictionaries. They can correctly identify and spell complex terminology, drug names, and anatomical parts that are easy to mistype.
This image really drives home how these benefits stack up in the real world, showing the direct impact on documentation time, error rates, and overall clinician satisfaction.
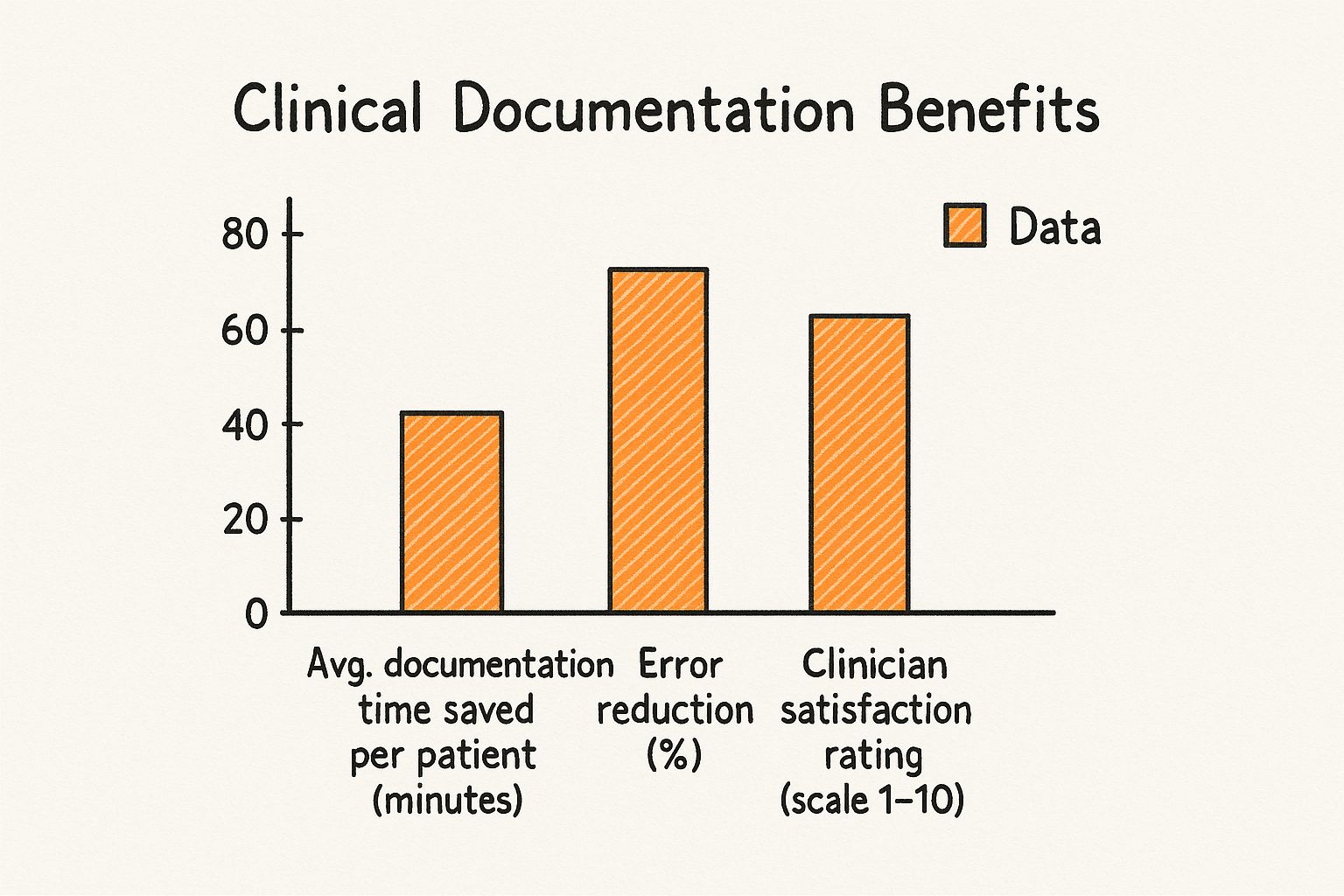
The data makes it clear: saving time and cutting down on errors are directly linked to a major increase in job satisfaction for clinicians. The power behind this effectiveness is often artificial intelligence, which is why it's worth exploring the broader innovations in healthcare artificial intelligence.
This table breaks down the core benefits in a clinical environment, illustrating how voice recognition delivers value across different operational areas.
| Benefit Area | Description | Impact on Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Efficiency | Automates the transcription of patient notes, orders, and communications, drastically reducing manual data entry time. | Clinicians reclaim up to two hours per day, allowing for more patient consultations and reduced administrative workload. |
| Enhanced Accuracy | Utilizes advanced medical vocabularies and AI to accurately capture complex terms, reducing typos and contextual errors. | Leads to more reliable patient records, fewer medical errors related to documentation, and improved patient safety. |
| Reduced Burnout | Alleviates the significant administrative burden of documentation, a primary contributor to stress and job dissatisfaction. | Improves physician well-being, increases job satisfaction, and helps retain experienced medical professionals. |
| Faster Turnaround | Enables real-time documentation, which accelerates the entire clinical cycle from diagnosis to treatment and billing. | Speeds up patient care delivery, improves revenue cycle management, and creates a more agile operational workflow. |
By addressing these key areas, voice technology not only improves processes but also fosters a more sustainable and positive work environment for medical staff.
The crushing weight of administrative tasks is one of the biggest drivers of burnout in the medical field. When doctors are spending nearly as much time on paperwork as they are with patients, it’s no surprise that job satisfaction takes a nosedive. This is where voice technology delivers perhaps its most meaningful benefit.
By automating the tedious, repetitive task of documentation, voice recognition software directly targets a major source of stress and fatigue. It allows clinicians to actually leave work at a reasonable hour without a pile of charts hanging over their heads, which is huge for work-life balance.
This isn’t just about feeling better; it’s about career longevity and the quality of care itself. A physician who is less stressed and more engaged is naturally better equipped to provide compassionate, attentive care.
The numbers back this up. The global market for voice recognition in healthcare is expected to climb from USD 8.53 billion to USD 19.57 billion by 2030, a powerful growth rate reflecting just how valuable this technology has become. It’s helping create healthier, more sustainable clinical environments by tackling efficiency and accuracy, ultimately helping to bring the focus of medicine back to where it always should have been: on the human connection between a doctor and their patient.
The real magic of voice recognition software in healthcare isn't just that it turns speech into text—it's how it adapts to the unique pressures and workflows of different medical fields. This isn't a one-size-fits-all gadget. It's more like a specialized instrument that gets fine-tuned for the specific job at hand.
When you see how it works in different areas, you start to understand its true potential. It moves from being a cool piece of tech to a genuine problem-solver.

Whether it’s the controlled chaos of an emergency room or the meticulous detail of a radiology reading room, voice recognition has a role to play. It directly tackles the documentation headaches each specialty faces, which in turn improves how smoothly things run, how accurate the records are, and ultimately, how well patients are cared for.
Let's look at a few real-world examples.
A radiologist's world is one of immense detail and tight deadlines. They spend their days poring over complex images—MRIs, CT scans, X-rays—and then have to produce incredibly detailed reports that other doctors depend on for life-or-death decisions. The old way of doing things, dictating findings and then waiting for someone to type them up, creates a frustrating delay that can slow down patient care.
Now, picture a radiologist using modern voice recognition. As they analyze a scan, they're dictating their findings directly into a report. The software, which has been trained on a massive vocabulary of radiological terms, captures every nuance—from intricate descriptions of tissues to precise measurements of lesions—with over 99% accuracy.
Because the documentation happens in real time, reports can be finalized just minutes after the images are reviewed. This slashes the turnaround time for diagnoses, meaning treatments can start hours, or sometimes even days, earlier.
The emergency department (ED) is organized chaos. Clinicians are juggling multiple critical patients at once, and stopping to document care feels like an impossible luxury. Yet, those records are non-negotiable for ensuring continuity of care and for legal reasons.
This is where voice recognition software for healthcare becomes an absolute game-changer. It allows for hands-free documentation right in the middle of the action. An ED doctor treating a trauma patient can verbally command the system to order labs, request medications, and log procedures as they're happening.
For instance, while working on a patient, a physician might say, "Order a CBC, basic metabolic panel, and a CT of the abdomen and pelvis." The system doesn't just type that out; it can be set up to route those orders straight to the lab and imaging departments.
Voice recognition allows clinicians to capture critical information at the point of care, not hours later when details get fuzzy. This makes patient handoffs safer and the medical record far more reliable.
The heart of primary care is the relationship between the doctor and the patient. That relationship suffers when the doctor is forced to stare at a computer screen, typing away instead of listening. It's a common complaint from patients: "My doctor spends more time with the computer than with me."
This is where a more advanced form of voice recognition, known as ambient clinical intelligence, is making a profound difference.
Imagine this: a doctor and patient are having a completely normal conversation. A small, secure ambient listening device in the room captures their discussion. The AI behind the scenes gets to work, processing the entire dialogue and distinguishing between the doctor's voice and the patient's.
From that natural conversation, the software intelligently pulls out all the key clinical data:
The system then takes that information and automatically organizes it into a structured clinical note in the EHR. All the physician has to do is give it a quick review and sign off. This frees them up to maintain eye contact, build trust, and focus 100% on the person in front of them. It completely changes the dynamic of the visit for the better.
Voice recognition software is only as good as its connection to your core systems. To have any real impact in a clinic or hospital, it can't just be another piece of software running in the background—it has to plug directly and seamlessly into your Electronic Health Record (EHR) system.
Think of the EHR as the central hub for all patient information. Any new tool you introduce needs to feel like a natural extension of it, not some clunky add-on that creates more work.
A standalone voice tool that forces a clinician to dictate text and then copy-paste it into the EHR is worse than useless. It adds extra steps, opens the door for errors, and completely misses the point of saving time. True integration means the voice software and the EHR are in constant communication, instantly and securely sharing data. This creates a smooth workflow where a doctor’s dictated notes, prescriptions, and orders automatically land in the right fields within the patient’s chart.

This direct link is what transforms clinical documentation from a manual chore into an automated, almost invisible process. Without it, you’re just swapping one tedious task for another.
The magic behind this seamless connection is a concept called interoperability. It's just a technical way of saying that different software systems can talk to each other and understand one another. Here, it’s all about making sure your voice recognition software speaks the same language as your EHR. This is usually handled through an Application Programming Interface, or API.
Think of an API as a secure messenger between the two systems. When a doctor speaks a note, the voice software uses the API to package that information and send it directly to the EHR, which knows exactly where to file it.
The best voice recognition solutions are built for this from the ground up and often have ready-made integrations for major EHR platforms like:
These established connections ensure data flows securely and reliably, following strict healthcare data standards like HL7 (Health Level Seven).
The whole point of integration is to make the technology disappear. A clinician shouldn't have to think about the software at all. They should just be able to speak naturally and trust that the information is being captured correctly in the system they already live in every day.
This push for deep EHR integration is fueling massive market growth. The EHR speech recognition market is on track to hit around USD 62.9 billion by 2035, growing at a compound annual rate of 7.5%. This boom is driven by the urgent need for hospitals to make documentation faster and slash transcription errors. You can get more market insights from the full report on Future Market Insights.
Even with a flawless technical link, the job isn't done. Integration is also about people and processes. No two clinics or hospital departments work the same way, so a successful rollout means the voice recognition system must bend to fit your specific workflows—not the other way around.
This often comes down to mapping custom voice commands to specific actions inside the EHR. For example, a family doctor might need a simple command like "new patient note" that opens a chart and puts the cursor in the "reason for visit" field. A surgeon, on the other hand, might need a command like "pull up pre-op checklist" that navigates to a completely different screen.
Here are a few practical steps to nail the integration process:
By focusing on both the technical connection and the human element, you can ensure your voice recognition software for healthcare becomes an asset that truly helps your clinicians, rather than hindering them.
In healthcare, data is more than just information—it's a patient's story. That's why protecting Protected Health Information (PHI) is absolutely critical. When you bring voice recognition software for healthcare into the mix, adhering to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) isn't optional; it's the law.
The second a patient's voice is recorded, it becomes PHI. This means the software handling it needs ironclad security built in from the very beginning.
Think of it like a digital vault. Every step, from the moment a doctor speaks into a microphone to the final transcribed note landing in the EHR, has to be protected. Reputable software vendors don't just put one lock on the door; they build a fortress of defenses to keep patient privacy intact.

When you're shopping for a voice recognition tool, certain security features are non-negotiable. These are the fundamentals of any truly HIPAA-compliant system.
Under HIPAA, any vendor that touches your PHI is known as a "Business Associate." This legal distinction means you are required to have a formal Business Associate Agreement (BAA) signed with your voice recognition provider.
A BAA is a legal contract that clearly spells out how a vendor will protect PHI. It’s your organization's formal guarantee that your partner is just as committed to HIPAA's strict standards as you are.
This document is your safety net. It details the vendor's responsibilities and outlines the exact procedure for reporting a data breach. Working without a signed BAA is a massive compliance risk for your organization. To keep everything organized, many facilities use dedicated healthcare compliance software to manage BAAs and other regulatory paperwork.
To make sure you're covering all your bases, here’s a quick checklist to use when evaluating a potential software partner.
| Compliance Area | Key Feature/Question | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Is all data encrypted both in transit and at rest using strong, current standards (e.g., AES-256)? | Protects PHI from being read or stolen if intercepted by unauthorized parties. |
| Access Control | Does the platform support multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls (RBAC)? | Ensures only authorized users can access sensitive data, preventing internal and external breaches. |
| Audit Trails | Are detailed logs kept of all user activity, including who accessed PHI, when, and what they did? | Provides a crucial record for investigating security incidents and demonstrating compliance during audits. |
| Business Associate Agreement | Will the vendor sign a comprehensive BAA that clearly outlines their responsibilities under HIPAA? | A BAA is a legal requirement. Without it, your organization is non-compliant and liable for the vendor's actions. |
| Secure Data Centers | Are the servers hosted in a physically secure, independently audited environment (e.g., SOC 2, HITRUST)? | Verifies that the vendor's infrastructure meets high standards for security, availability, and privacy. |
| Data Breach Protocol | Does the BAA specify a clear process and timeline for notifying you in the event of a data breach? | Ensures you can respond quickly to a security incident to mitigate harm and fulfill your own legal reporting duties. |
By prioritizing these security measures and formalizing your partnership with a BAA, you can adopt voice recognition technology with confidence. The goal is to unlock powerful new efficiencies without ever gambling with patient privacy.
Picking the right voice recognition partner can feel a little like navigating a maze. The market is packed with options, and it’s tough to know where to start. To get it right, you need a clear game plan that looks past the flashy sales pitches and focuses on what actually matters for your clinical and operational needs.
The goal here isn't just to buy a piece of software; it's to make a long-term investment in your team's efficiency and job satisfaction. A smart choice now will pay off for years to come. That means you need to be systematic when you start comparing vendors.
When you're looking at different types of voice recognition software for healthcare, a few key factors should be at the top of your list. These are the things that separate a basic tool from a genuine clinical documentation partner.
There's a reason so many vendors are jumping into this space. The global medical speech recognition market is on track to hit USD 5.58 billion by 2035, growing at a healthy clip of 11.21% each year. This boom is fueled by the relentless demand for smarter clinical tools that play nicely with major EMR systems. You can dig deeper into this trend and its key players in this medical speech recognition market report.
Another fork in the road is deciding where the software will live. Each option—hosting it yourself or using the cloud—has its own set of trade-offs when it comes to cost, control, and maintenance.
On-Premise:
This is the traditional route, where you host the software on your organization's own servers.
Cloud-Based (SaaS):
With this model, the vendor hosts everything, and you access it over the internet, usually for a monthly or annual subscription fee.
For most modern healthcare organizations, a secure, HIPAA-compliant cloud solution offers the best mix of flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. It frees you up to focus on patient care instead of server upkeep.
Finally, don't ever skip the trial run. Reading brochures and watching demos is one thing, but the only way to truly know if a solution fits is to let your team put it through its paces in their daily work.
A pilot program gives you the real-world feedback you simply can't get anywhere else.
Diving into voice recognition for healthcare naturally brings up some important questions. Let's tackle a few of the most common ones to give you a clearer picture of how this technology works in a real-world clinical environment.
It's surprisingly accurate. Today's top-tier voice recognition software for healthcare often hits over 99% accuracy right from the start. This isn't your average consumer voice assistant; these systems are trained on vast datasets of medical jargon—from complex drug names to specific anatomical terms and procedures.
Of course, a few things can affect performance:
The great thing is that most systems get smarter over time. They learn your unique voice, pronunciation, and common phrases, becoming even more accurate the more you use them.
Not always, and this is a critical point. While many voice recognition tools aim for broad compatibility, you can't assume a seamless connection with every Electronic Health Record (EHR) system.
The best platforms have deep, out-of-the-box integrations with major EHRs like Epic, Cerner, and Athenahealth. A "deep integration" means the software can do more than just paste text; it can intelligently populate specific fields, navigate menus, and place orders directly within the EHR.
Before you choose a solution, you absolutely must verify that it has a proven, stable integration with your specific EHR. Ask for documentation or case studies to see it in action.
If there isn't a pre-built connection for your EHR, many vendors can use APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to build a custom one, but this often involves a bit more technical legwork.
Patient privacy is baked into the core design of any reputable medical voice recognition tool. HIPAA compliance is the absolute minimum standard, and vendors use a multi-layered approach to keep data safe.
First, all data—both the audio of your voice and the transcribed text—is protected by end-to-end encryption. This means it's scrambled and unreadable while it's being sent to the server and while it's stored.
Second, vendors host their services in highly secure data centers that undergo rigorous independent security audits. Finally, the relationship is always governed by a Business Associate Agreement (BAA), which is a legally binding contract that holds the vendor accountable for protecting any patient health information they handle.
Ready to integrate fast, accurate, and affordable transcription into your healthcare application? Lemonfox.ai offers a developer-friendly Speech-to-Text API with exceptional accuracy across over 100 languages. Start your free trial today and discover a cost-effective solution for your transcription needs at https://www.lemonfox.ai.