First month for free!
Get started
Published 10/26/2025
The days of painstakingly typing out patient notes or waiting days for a transcription service are quickly coming to an end. Voice recognition software for medical transcription isn't some far-off idea anymore; it's a practical tool that’s making modern healthcare more efficient. Leading the way are flexible, API-first solutions like Lemonfox.ai.
This guide is a hands-on walkthrough, showing you exactly how to move from a sluggish, manual documentation process to a nimble system built around a powerful Speech-To-Text API.
It's no secret that administrative tasks weigh heavily on clinicians. This burnout is a real crisis, stealing precious time that should be spent on patient care. Traditional transcription, with its reliance on human typists, is often a major bottleneck—it's slow, costly, and can introduce errors.
AI-powered voice recognition tackles these problems head-on. It delivers instant, accurate, and scalable transcription that can keep up with the demands of a busy clinic.
This is about more than just swapping a keyboard for a microphone. It’s a complete overhaul of the clinical documentation workflow. A robust Speech-To-Text API allows healthcare providers to dictate patient encounters naturally and get structured, usable text back in seconds.
This unlocks a few key benefits:

To see just how big the difference is, let's compare the traditional approach with an AI-powered one.
| Feature | Manual Transcription | AI Voice Recognition (Lemonfox.ai) |
|---|---|---|
| Turnaround Time | Hours to days | Seconds to minutes |
| Cost | High per-minute or per-line rates | Significantly lower, usage-based pricing |
| Scalability | Limited by human workforce | Virtually unlimited, handles any volume |
| Accuracy | Variable, prone to human error | Consistently high, with continuous learning models |
| Workflow | Send audio, wait for return, review, import | Dictate, get instant text, quick edit, done |
The table makes it clear: AI isn't just a minor improvement; it fundamentally changes the economics and efficiency of clinical documentation.
The rapid move to this technology isn't just a trend; it's reshaping the entire market. The global medical transcription market is currently valued at nearly $90.32 billion and is expected to soar to $156.75 billion by 2030.
What’s driving this massive growth? Primarily, the integration of artificial intelligence. AI ambient scribe systems are projected to grow at a 15.02% CAGR, blowing past the growth rates of older methods. You can dive deeper into these medical transcription market trends and projections to see the full picture.
This transition represents one of the most significant opportunities to alleviate clinician burnout. By automating the most time-consuming parts of documentation, we give back precious minutes to every patient encounter, directly improving the quality of care.
Ultimately, bringing voice recognition software for medical transcription into your practice is a strategic decision. It’s a move toward a more efficient, affordable, and patient-focused model of care. The rest of this guide will give you the practical steps to make it happen.
Before you can write a single line of code to make an API call, you've got to get your house in order. A little prep work now saves a ton of headaches later, ensuring the whole integration process is secure and efficient.
This initial setup isn't about diving into complex algorithms; it's about building a solid foundation for your voice recognition software for medical transcription. The first, most critical step? Securing your credentials.
When you sign up for a service like Lemonfox.ai, they’ll give you a unique API key. Treat this key like the password to your entire application—it authenticates every request you make and ties it directly to your account. It goes without saying, but keep it confidential and never, ever expose it in client-side code.
With your key safely tucked away, it's time to carve out a workspace to build and test the integration. The great thing about the Lemonfox.ai API is that it's language-agnostic, but for these examples, we'll stick with Python. It's clean, simple, and has fantastic libraries for handling web requests.
I always recommend starting with a dedicated project folder and spinning up a virtual environment. This is a non-negotiable best practice. It isolates your project's dependencies, so you won't have to worry about library version conflicts with other projects on your machine. Trust me, this simple step will save you from a world of pain down the road.
Once your environment is active, you only need one core library to get going:
The Lemonfox.ai platform itself is designed to make this easy. The dashboard is clean and developer-focused, giving you quick access to your API keys, usage stats, and documentation right from the get-go.
Every API has rules of the road to ensure the service stays stable and available for everyone. These are called rate limits, and they dictate how many requests you can send within a certain period. Knowing these limits upfront helps you design your application to work within the rules, avoiding frustrating errors or temporary blocks.
For any medical application, security isn't just a feature—it's a requirement. Integrating voice recognition software for medical transcription demands a security-first mindset, especially concerning Protected Health Information (PHI).
Always double-check that your connection to the API is over HTTPS, which encrypts all data while it's in transit. Once you receive the transcribed text, the responsibility shifts to you. Your application must handle that output according to strict HIPAA guidelines for storage, access, and auditing.
While Lemonfox.ai securely processes the audio and deletes it immediately after transcription, your system is responsible for the compliant handling of the text on your end. This proactive stance on security and system setup is the bedrock of any reliable medical transcription workflow.
Alright, you've got the setup handled. Now it's time for the fun part—moving from theory to actually seeing this thing work. We're about to make our first real API call to see Lemonfox's voice recognition software for medical transcription do its magic on a clinical audio file.
To make this practical, we'll use a classic clinical scenario: a physician dictating a SOAP note right after a patient appointment. This isn't just a "hello world" test; it’s a direct look at how spoken medical notes become structured, useful data.
The whole process is surprisingly simple. Using the Python requests library we installed earlier, you're going to send an audio file straight to the Lemonfox.ai endpoint. The API takes it from there, churning through the audio and handing back a clean JSON response in just a few seconds.
Let's assume you have a recording of a dictated note saved as soap_note.wav. The Python code needed to get it transcribed is refreshingly minimal. All you need is your API key and the endpoint URL.
Here’s a basic script showing what that request looks like. Pay attention to how we open the audio file in binary mode ('rb') and pass it in the files payload. This is the standard, reliable way to handle file uploads in HTTP requests.
import requests
API_KEY = 'YOUR_LEMONFOX_API_KEY'
API_URL = 'https://api.lemonfox.ai/v1/audio/transcriptions'
audio_file_path = 'soap_note.wav'
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {API_KEY}'
}
with open(audio_file_path, 'rb') as audio_file:
files = {'file': audio_file}
response = requests.post(API_URL, headers=headers, files=files)
print(response.json())
This little script is the heart of your integration. Run it, and it will upload your soap_note.wav file and then print the complete transcription data right to your console.
The real power here isn't just getting text back; it's how you get it back. A successful request returns a JSON object, a universal format that’s a breeze for any programming language to understand. And it’s packed with more than just the raw words.
The metadata that comes with the transcript is just as crucial as the text itself. Things like timestamps and confidence scores are what let you build trust in the system and create efficient quality-control workflows for clinical staff.
A typical response from the API might look something like this (I’ve simplified it a bit for clarity):
{
"text": "Subjective patient complains of a persistent dry cough... Objective vital signs are stable...",
"words": [
{ "word": "Subjective", "start": 0.5, "end": 1.2, "confidence": 0.98 },
{ "word": "patient", "start": 1.3, "end": 1.8, "confidence": 0.99 },
{ "word": "complains", "start": 1.9, "end": 2.5, "confidence": 0.95 }
]
}
This structured data is where the magic happens. You can immediately pull out several key pieces of information:
text field gives you the complete, ready-to-use transcription.start and end times. This is perfect for building interactive transcripts where clicking a word jumps to that exact spot in the audio.confidence value (from 0 to 1) shows how certain the AI model is about each word it transcribed. A score of 0.99 is highly confident; a score of 0.75 might be worth a second look.Your next move is to parse this JSON. You can easily loop through the words array and find any terms with low confidence scores, automatically flagging them for a human to review. This hybrid model—letting the AI do the heavy lifting and having a human editor for verification—is the most effective path to achieving near-perfect accuracy in medical documentation.
Getting a basic transcript is one thing, but when it comes to clinical documentation, the stakes are much higher. A simple transcription mistake isn't just a typo; it can have real consequences for patient care. That's why getting your voice recognition software for medical transcription to understand the specific language of healthcare isn't just a nice-to-have, it's essential.
Historically, this has been a huge challenge. Even top-tier AI transcription platforms often fell short of human professionals, hovering around 61.92% accuracy. But things are changing fast. Modern systems, powered by deep learning and natural language processing, are now aiming for near-perfect transcription of complex medical terms and a wide range of accents. You can read more about these key trends in medical transcription to see where the industry is headed. The real leap forward comes from features that let you teach the AI the unique vocabulary your practice uses every single day.
One of the most powerful tools in your arsenal is the custom vocabulary feature. This isn't just a spell-checker; it's a way to build a dedicated list of words, phrases, and names that the API needs to know, even if they're not in a standard dictionary. For medical transcription, this is a total game-changer.
Think about the specialized language in a cardiology clinic. A generic transcription model will almost certainly stumble over terms like "echocardiogram," drug names like "atorvastatin," or the last names of referring physicians. By adding these to your custom vocabulary, you give the model the information it needs to get it right, dramatically boosting accuracy.
Here’s a real-world example of what that looks like. Without any customization, the API might hear a dictation and spit this out:
But once you’ve added "atorvastatin" to your custom vocabulary list, the output becomes what you actually need:
That one small tweak makes all the difference in creating a reliable and clinically accurate document.
Think of your custom vocabulary list as a living document. It's not a set-it-and-forget-it task. As new drugs, procedures, or medical devices become part of your workflow, you should be adding them to the list. This is how you ensure the transcription model evolves right alongside your practice.
Clinical conversations are rarely one-sided. A physician is often dictating notes while also talking to a patient or another member of the staff. This is where speaker diarization (sometimes called speaker recognition) becomes incredibly valuable.
This feature is smart enough to analyze the audio and split the conversation into different speaker channels. Instead of getting a confusing, jumbled block of text where every voice is mashed together, you receive a clean, organized transcript that clearly labels who said what.
Just imagine this common scenario:
That separation is crucial. It’s the key to creating accurate patient records and making sure a patient's own words aren't accidentally documented as part of the physician's official assessment.
Finally, always remember the golden rule: garbage in, garbage out. The quality of your transcription is directly linked to the quality of the audio you feed the system. Taking a few moments for some basic audio pre-processing can make a massive difference in your results.
By combining these three strategies—a robust custom vocabulary, smart speaker diarization, and clean audio input—you’re no longer just using a standard transcription tool. You're building a highly accurate clinical documentation assistant that's truly tailored to your needs.
Getting a highly accurate transcript is a great first step, but it's not the end of the road. The real magic happens when that transcript is seamlessly integrated into your existing clinical workflow. We're not just aiming for a block of text; we're building a complete system that bridges the gap between the Lemonfox.ai API's output and your team's day-to-day operations. This means creating an intuitive space for clinicians to review, edit, and sign off on AI-generated notes.
This is what's often called a "human-in-the-loop" model, and for good reason—it’s the gold standard for using voice recognition software for medical transcription. You get the sheer speed of AI paired with the irreplaceable judgment of a medical professional. This combination ensures every single document is 100% accurate before it ever touches a patient’s official record. When designed right, this entire review process can feel practically effortless.
The infographic below shows how the whole process starts, even before the first word is transcribed. It's all about optimizing the audio from the get-go.
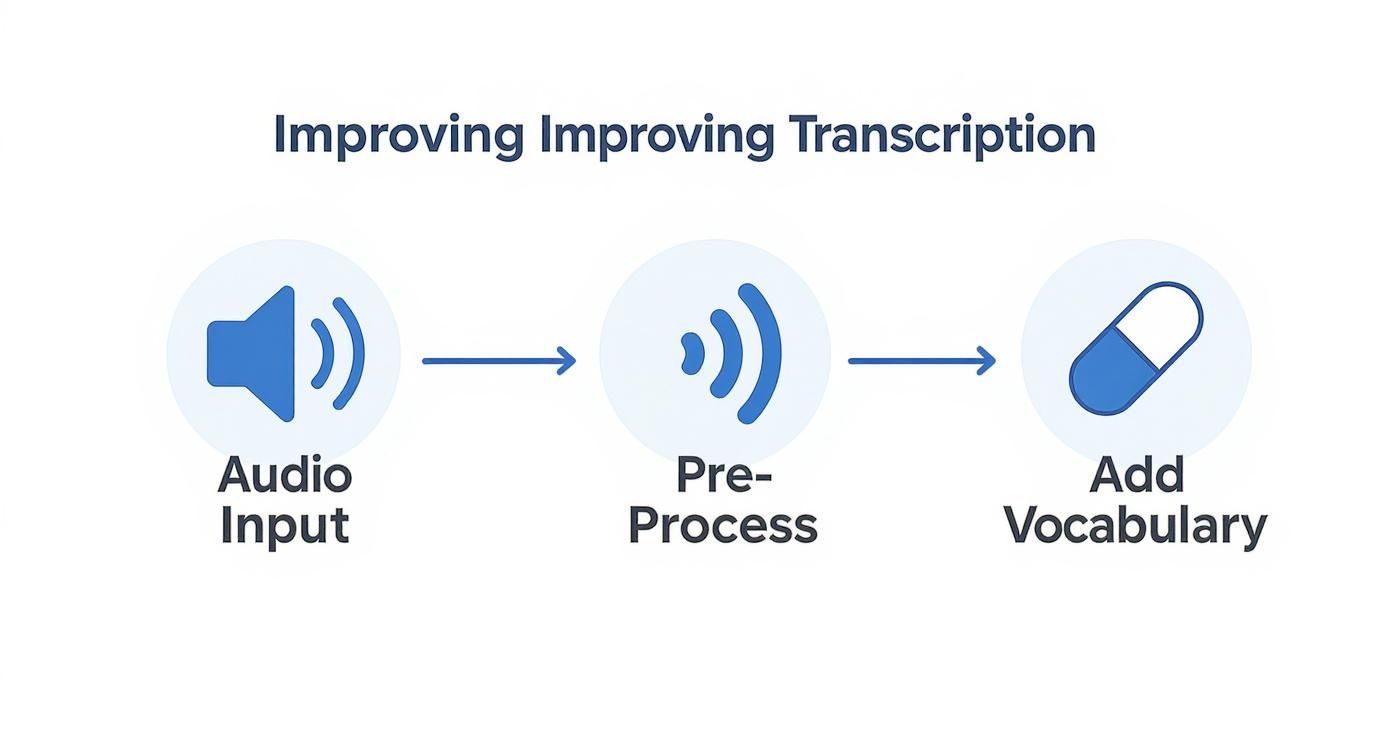
As you can see, the quality of your input audio has a direct impact on the accuracy of the output, which in turn makes the rest of the workflow that much smoother.
At the heart of a solid workflow is a user-friendly interface. Think simple: the transcribed text on one side, and the original audio player right next to it. This setup empowers any medical professional—a doctor, nurse, or MA—to quickly listen to a specific part of the dictation and make any necessary corrections on the fly.
But we can make it even smarter. The best interfaces use the metadata returned by the API, especially timestamps and confidence scores. Imagine automatically highlighting any word with a confidence score below a certain threshold, say 0.85. This little trick instantly draws the reviewer's eye to the exact spots where the AI might have struggled. What could have been a long, tedious proofreading session becomes a quick scan of a few flagged words.
The goal here isn't to replace your team's expertise but to supercharge it. By automatically flagging potential errors, you change the task from mind-numbing proofreading to a quick, high-value verification step. It's a huge time-saver.
Once a transcript gets the green light, the last piece of the puzzle is getting it into the patient's Electronic Health Record (EHR). Manually copying and pasting is a non-starter. It’s slow, tedious, and a prime opportunity for human error to creep in. A truly end-to-end workflow automates this final, crucial handoff.
Luckily, most modern EHR systems provide their own APIs. You can build a straightforward integration that, with a single "Approve" click in your review interface, sends the final, polished text directly to the correct patient chart. No fuss, no mistakes.
To pull it all together, think about the integration process in these distinct stages.
| Workflow Stage | Objective | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Capture | Obtain a crystal-clear recording of the clinical dictation. | Use a quality microphone in a room with minimal background noise. |
| API Transcription | Generate the initial text draft along with useful metadata. | Send the audio file over to the Lemonfox.ai API for processing. |
| Human Review | Verify accuracy and correct any AI-generated mistakes. | Use an interface with synced audio playback and flagged low-confidence words. |
| EHR Integration | Securely push the approved documentation to the patient's chart. | Trigger an API call to your EHR system once the "Approve" button is hit. |
This complete cycle—from a clinician's spoken words to a finalized entry in the patient record—fully closes the documentation loop. It elevates the API from a simple transcription tool to a powerful engine that drives efficiency, slashes errors, and, most importantly, gives clinicians back their most valuable asset: time.
Whenever we bring a new piece of technology into a clinical environment, a healthy dose of skepticism is expected. It's only natural. When it comes to using voice recognition for medical transcription, the questions I hear most often circle around patient data security, how the tech handles different accents, and whether it’s actually worth the cost. Let’s tackle these head-on.
This is the big one, and for good reason. In healthcare, security isn't just a feature; it's a foundational requirement. Any transcription tool you use absolutely must be compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
When you work with an API provider like Lemonfox.ai, the first thing you need is a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). This is the legal cornerstone that obligates the provider to uphold stringent security measures when dealing with Protected Health Information (PHI).
Modern, well-designed APIs are built from the ground up for this. Think of it this way: the data is encrypted as it travels from your system to theirs, and it's encrypted again while being processed. Critically, services like Lemonfox.ai are often designed to process the audio and immediately purge it from their servers. This "no-trace" approach is a huge win for privacy because it drastically reduces the data footprint.
Keep in mind, HIPAA compliance is a two-way street. While the API provider secures their end of the process, your organization is still responsible for making sure your own systems—where the finished transcripts live—are locked down and compliant.
This is probably the most practical question I get asked. After all, a tool that can't understand every one of your clinicians is essentially useless. The good news is that the technology has come a very long way.
Today's voice recognition engines are trained on absolutely massive datasets. We're talking about a vast collection of audio that includes a huge variety of global accents, unique dialects, and individual speaking styles.
This training makes them surprisingly good at understanding accented speech right from the get-go. No system is 100% perfect, of course, but you’ll find the performance is incredibly solid. To get the absolute best results, I always recommend a few simple best practices:
From a purely financial perspective, the case for an API-driven solution is hard to argue with. Traditional transcription services usually bill you by the line or by the word. For a busy practice, those costs add up fast.
An API, on the other hand, typically charges per minute of audio. It's a much more scalable and predictable model. For example, a service like Lemonfox.ai can process audio for less than $0.17 per hour, which is a fraction of the cost of manual transcription.
What I've seen work best in the real world is a hybrid approach. The AI does the heavy lifting, creating a highly accurate first draft in just a few seconds. Then, a human editor gives it a quick final polish. This "human-in-the-loop" workflow gives you the best of both worlds: the incredible speed and low cost of AI, plus the peace of mind that comes with a final human review.
Ready to see how an affordable, accurate, and secure API can transform your clinical documentation workflow? Get started with Lemonfox.ai and experience the future of medical transcription. Explore the API and start your free trial today.