First month for free!
Get started
Published 10/30/2025

Prosody is the music of speech—it’s not about the words you choose, but how you say them. Think of it as the rhythm, stress, and intonation that breathes life, emotion, and true meaning into your voice. It’s what turns a flat line of text into a vibrant, compelling message.

Have you ever asked someone how they are, and they replied, "I'm fine," but you knew instantly they weren't? The words were positive, but the delivery—maybe a flat tone, a slight downward pitch, or a heavy sigh—told the real story. That powerful, unspoken layer is prosody in action.
It’s the very thing that allows us to pick up on sarcasm, feel a speaker's excitement, or sense urgency in their voice. Without it, our conversations would sound eerily robotic and monotone, completely stripped of the emotional context that makes human connection possible.
To really get a handle on prosody, it helps to break it down into its three core components. Each one plays a distinct role in shaping the music of our speech.
| Element | What It Controls | How You Hear It |
|---|---|---|
| Intonation | The rise and fall of your voice's pitch. | A rising pitch at the end of a question, or a falling pitch to signal a statement. |
| Stress | The emphasis or prominence placed on certain syllables or words. | Saying "I want to go" versus "I want to go" to change the meaning. |
| Rhythm | The timing, pacing, and pausing between words. | A fast, hurried pace conveying excitement, or long pauses for dramatic effect. |
Together, these three pillars work in harmony to give our speech its unique texture and meaning, telling listeners not just what we're saying, but how they should feel about it.
Let’s look at a classic example to see just how much work prosody does. Take this simple sentence: "I didn't say he stole the money." On the surface, it’s a straightforward denial. But watch what happens when we shift the stress:
See? The same seven words can have at least four different meanings, all depending on which word gets the spotlight. The melody carries as much—if not more—information than the lyrics.
This idea isn't new. The study of prosody actually dates back to ancient Greece, where it was first used to describe word accents. Over the centuries, linguists expanded the definition to cover the rich combination of rhythm, pitch, and pausing we recognize today. You can read more about the origins of prosody and how its definition has evolved).
The Key Takeaway: Prosody is the brain's instruction manual for speech. It tells the listener how to interpret the words, clarifying intent, revealing emotion, and preventing a world of miscommunication.
Grasping what prosody is in speech is the first step toward becoming a more perceptive communicator. It’s also fundamental to understanding the technology behind the voice assistants we talk to every day.
Prosody isn't one single thing you can point to in speech. It’s more like a symphony, where several distinct elements come together to create meaning and emotion. Just as a composer uses melody, rhythm, and volume to bring a piece of music to life, a speaker does the same thing with their voice.
To really get what prosody is and how it works, we need to look at its core components. Let's break down the three main building blocks: intonation, stress, and rhythm. Each one adds a unique layer, turning plain words into rich, expressive communication.
Think of intonation as the rise and fall of your voice's pitch when you talk. It's the melodic shape of our sentences, and it often does the heavy lifting of signaling the difference between a statement and a question without changing a single word. In many ways, it's the punctuation of spoken language.
Let's take a simple phrase: "You're going to the store."
This musicality in our voice is also how we broadcast our feelings. A high, rising pitch can signal excitement or surprise, while a low, flat tone might suggest boredom or sadness. Without intonation, we'd all sound robotic and monotone, and it would be incredibly hard to figure out what anyone was really thinking or feeling.
Intonation provides the emotional and grammatical roadmap for our words. It’s the difference between stating a fact, asking a question, and expressing total disbelief, all using the exact same sequence of words.
Stress is all about which words or syllables you choose to emphasize in a sentence. By putting a little extra punch on certain words, you can completely change the listener's focus and, ultimately, the meaning of what you're saying. It’s like using a spotlight to draw the audience's attention to the most important actor on stage.
Let’s go back to a classic example: "I didn't say he stole the money." Watch how the meaning shifts depending on where you place the stress:
Each version guides the listener to a different conclusion by highlighting what's most important. This is so fundamental that in English, speakers with certain speech disorders, like apraxia, can struggle with typical stress patterns. They might place equal stress on every syllable, which can make their speech sound unnatural and tough for others to follow.
Finally, we have rhythm. This is the pacing, timing, and pausing that creates the overall cadence of our speech. A good, steady rhythm makes speech feel natural and easy to listen to, kind of like how a steady beat in a song makes you want to tap your foot. It’s all about the pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables and the smart use of silence.
Rhythm is how we control the flow of information. A speaker might speed up their pace to show excitement or urgency. On the flip side, they might slow right down and use deliberate pauses to build suspense or to make sure a key point really lands. This flow is also crucial for navigating conversations; subtle shifts in rhythm can signal to the other person that you're about to wrap up your thought, giving them the cue to jump in.
It’s one thing to know the nuts and bolts of prosody, but it's another thing entirely to appreciate just how much it shapes our daily lives. Think about it: prosody is the only reason you can tell a genuine compliment from a sarcastic dig, even when the exact same words are used.
It's how we inject emotion into what we say. Without even thinking, you use it to show excitement, express empathy, or signal frustration—all without ever changing the script.
Consider a tricky negotiation or just trying to figure out what a friend is really thinking. The tiny shifts in their pitch, the way they pause, or the words they choose to emphasize all provide a hidden layer of meaning. This unspoken data often says more than the words themselves, cutting through ambiguity and helping you connect on a deeper level.
Prosody also acts as the invisible traffic cop in our conversations. It’s what helps us manage turn-taking, creating those smooth, seamless transitions where one person stops talking and another one picks up right on cue. A slight dip in pitch and a final pause is a universal signal for "I'm done, your turn."
On the flip side, holding your pitch steady and avoiding long pauses tells your listener, "Hang on, I've got more to say." We've been using these signals our whole lives, and we process them automatically. Without them, our conversations would quickly dissolve into a chaotic jumble of interruptions and awkward silences.
This map helps visualize how the core elements—intonation, stress, and rhythm—all come together to create the "music" of speech.
Think of each element as a different instrument in an orchestra. Individually they're important, but only when they work together do you get the full, rich sound that conveys deep meaning.
The impact of prosody reaches far beyond casual conversations. It plays a surprisingly critical role in highly specialized fields. In clinical settings, for example, analyzing a person's prosodic patterns is a key part of assessing their pragmatic communication skills.
Key Insight: Truly effective communication isn't just about the words you choose. It's about the emotional and contextual information you transmit along with them. Prosody is the invisible force that shapes perception, clarifies intent, and ultimately builds stronger human connections.
Challenges with prosody are frequently linked to certain neurological conditions. In fact, prosody has become an important tool for understanding conditions like schizophrenia, where these pragmatic abilities can be impaired. This shows just how fundamental prosody is to our communication, both in typical interactions and clinical diagnostics. You can find more details about prosody's role in clinical assessments on pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
At the end of the day, understanding what prosody is in speech isn't just an academic exercise—it’s a communication superpower. When you learn to listen for the music behind the words, you unlock a much richer, more profound level of understanding in every single interaction.
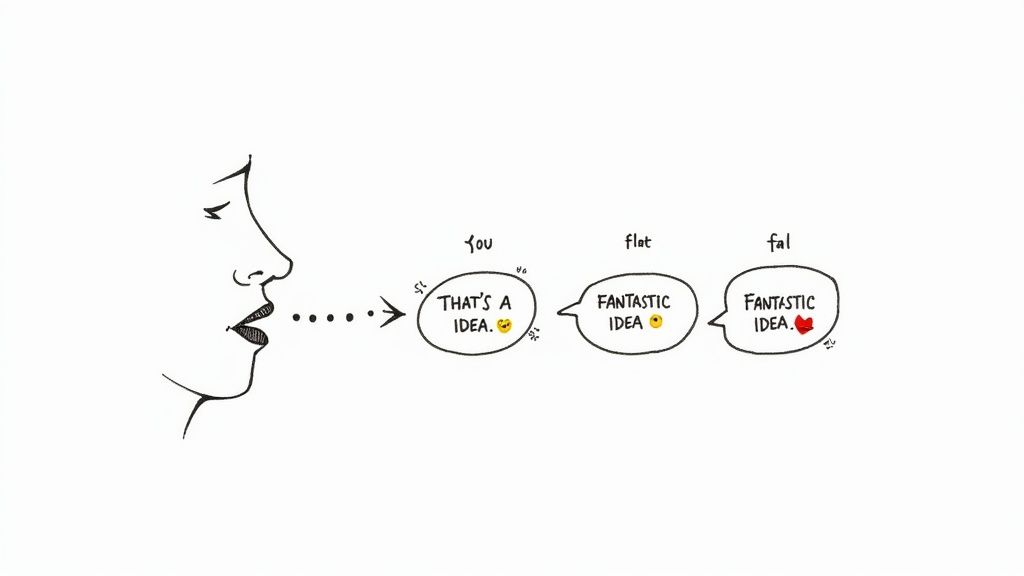
Once you know what to listen for, you'll start noticing prosody everywhere. It’s the invisible conductor of our daily conversations, the media we consume, and the speeches that grab our attention. This "music" of speech is what separates a heartfelt compliment from a sarcastic jab, even when the words are exactly the same.
Let’s look at a simple phrase and see how prosody can completely flip its meaning on a dime:
"That's a fantastic idea."
The text doesn't change, but the prosodic packaging transforms the message from wholehearted support to total mockery. This is prosody in action—the essential layer that adds emotional context and reveals true intent.
Ever notice how truly masterful public speakers can hold an entire room in the palm of their hand? They aren't just reading information off a slide. They are conducting an emotional experience with their voice, and prosody is their instrument.
Think of speakers like Brené Brown or the late Steve Jobs. They were experts at using rhythm and pausing to build suspense. A well-timed silence can hit an audience harder than any word, creating a pocket of tension or giving a profound point the space it needs to land. This command over the flow of speech is what keeps listeners hanging on every word.
Key Insight: Great speakers play their voice like an instrument. They shift their pitch to convey passion, use stress to make key ideas pop, and manage their rhythm to guide the audience’s emotional journey.
Barack Obama is another fantastic example, famous for his deliberate cadence and almost musical intonation. He uses a falling pitch to deliver statements with a sense of finality and authority, then switches to a rising pitch for rhetorical questions that pull you into the conversation. His use of stress is just as intentional, making sure the most important words in a sentence resonate with maximum impact.
When you start analyzing speech this way, you realize prosody isn't just some abstract linguistic concept. It’s a practical, powerful tool we all use—and can learn to use better—to connect, influence, and communicate far more than words alone ever could.

This sneak peek into Google's Text-to-Speech service shows just how granular voice synthesis has gotten. We can now tweak pitch, speaking rate, and even audio profiles for specific devices. These are all manual levers we can pull to control the elements of prosody, aiming for a voice that sounds right for the situation.
For decades, the voices coming out of our gadgets were flat, robotic, and painfully artificial. We always knew we were talking to a machine. The missing ingredient? Prosody.
Early text-to-speech (TTS) systems were pretty good at pronouncing individual words. But they had no idea how to string them together with the natural melody, rhythm, and stress that we humans use without a second thought. This left us with speech that, while technically understandable, was emotionally hollow and tiring to listen to. The jump from those old GPS voices to modern assistants like Alexa is a direct result of cracking the code of what prosody is in speech.
The game has changed completely. Modern AI voice synthesis isn't just about turning letters into sounds anymore. It’s about predicting and generating the perfect prosodic contour for any sentence, which is really the final frontier in making AI sound truly human.
To get there, developers feed complex neural networks gigantic datasets of human speech. These models aren't just memorizing words; they're learning the incredibly subtle relationships between sentence structure, context, and the resulting vocal patterns.
This is a massive undertaking. Prosody is a deeply complex mix of acoustic variables. To create a believable performance, the AI has to perfectly model pitch, loudness, duration, and even vocal timbre all at once. For a deeper dive into this, you can find more on the scientific complexity of prosody on en.wikipedia.org).
The Big Challenge: Teaching a machine the unwritten rules of human emotional expression is a monumental task. AI has to learn not just what words mean, but the entire spectrum of feeling they can carry through sound.
But this isn't just about making machines talk better; it's also about making them better listeners. Speech-to-text (STT) systems, like those from providers such as Lemonfox.ai, depend on prosodic cues to make their transcriptions more accurate and readable.
Think about it. When you talk, your pauses and pitch changes are punctuation clues. A slight pause often signals a comma. A longer one with a drop in pitch usually means the end of a sentence. And that classic rising pitch at the end of a phrase? It's a dead giveaway for a question mark.
By analyzing these prosodic markers, the best STT services can automatically add punctuation, transforming a raw wall of text into a coherent, useful transcript. This is a huge leap—moving from just transcribing words to actually interpreting intent. The quest continues to teach machines not just our language, but the beautiful, nuanced music behind it.
We've spent this guide pulling back the curtain on the hidden music of language. What we've found is that prosody isn't just some dusty academic term; it’s the very soul of how we communicate. It's the lifeblood that gives our words meaning, emotion, and impact.
We saw how its key ingredients—intonation, stress, and rhythm—blend together to turn a flat string of words into a rich, meaningful message. This is the stuff that separates a monotonous sentence from a compelling story.
Think about it. Understanding prosody is like gaining a superpower. It helps you catch the sarcasm in a friend's joke, feel the passion in a leader's speech, and know when "I'm fine" doesn't actually mean everything is fine. This insight doesn’t just make you a better listener; it sharpens your own ability to connect and persuade.
Final Takeaway: Start paying attention to how people speak, not just what they say. Listen for the rise and fall of their voice, the words they emphasize, and the cadence of their sentences. This simple shift in awareness is the first step to becoming a more empathetic and influential communicator.
We also touched on how modern technology is in a race to master this quintessentially human skill. The goal is to teach AI not just to mimic our words, but to truly understand and replicate their underlying melody.
By tuning your ear to prosody, you're doing more than just improving your speaking skills. You're unlocking a more profound understanding of human connection itself.
It's one thing to understand what prosody is, but another to see how it works in the real world. Let's tackle some of the most common questions that come up when people start digging into the music of speech.
You absolutely can. Think of it like learning to play an instrument. At first, you might be a bit clunky or monotonous, but with practice, you develop a natural, expressive flow. The idea is to break free from a flat delivery and learn to use your voice to truly engage people.
Here are a few practical ways to train your prosodic "muscles":
Not exactly. While every language on Earth uses prosody, the rules for how it's used can be wildly different from one culture to another. The basic ingredients are the same, but the recipe changes.
For instance, in English, we change our pitch (intonation) to ask a question versus making a statement. It adds a layer of meaning. But in a tonal language like Mandarin Chinese, the pitch you use can completely change a word's core definition. The syllable "ma" can mean "mother," "horse," or "to scold," all depending on the pitch contour you use.
The Bottom Line: In English, prosody provides emotional and grammatical clues. In tonal languages, prosody can be the difference between saying one word and a completely different one.
This is a great question, and it's easy to get them mixed up. The simplest way to remember it is that tone of voice is the result you get from using prosody.
Prosody is the technical toolkit—it's the nuts and bolts of intonation (pitch), stress (emphasis), and rhythm (timing and flow). It's the "how" of speaking.
Your tone of voice is the emotional flavor that this toolkit creates. When you use prosodic features like sharp stress, a quick pace, and a loud volume, you create an "angry" tone. So, prosody is the cause, and tone is the effect.
Ready to put the power of natural-sounding speech to work? Lemonfox.ai delivers fast, precise, and surprisingly affordable Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech APIs that master these nuances. Explore our APIs and start your free trial today.