First month for free!
Get started
Published 11/23/2025
Ever wondered how your phone can read an article out loud or how your GPS gives you turn-by-turn directions? That’s voice synthesis at work. Simply put, it's the technology that turns written text into spoken words, giving machines a human-like voice.
It's the digital voice behind your smart assistant, the narrator of your favorite audiobook, and the friendly guide on a customer service call. Essentially, it’s how technology learns to talk.
You probably use voice synthesis every day without even thinking about it. This process, also known as Text-to-Speech (TTS), is way more than just a computer reading words off a screen. Behind the scenes, complex algorithms and AI models are working to decipher not just the words, but the context, pronunciation, and even the emotional tone.
Think of it like training a computer to be a skilled voice actor. It doesn't just see the letters in "Hello." It learns the subtle nuances of human speech—the slight rise in pitch at the end of a question, the perfect pause for emphasis, and the natural rhythm that makes a voice sound alive. This ability to capture human intonation is what makes today’s AI voices so much better than the flat, robotic speech from a few decades ago.
So, how does a line of text become a spoken word? It’s a multi-step journey. Early systems often sounded clunky and mechanical because they were piecing together pre-recorded sounds. Today’s technology is far more sophisticated, learning from massive datasets of human speech to generate incredibly realistic voices.
To pull this off, a modern TTS system has to get three key things right:
The ultimate goal of voice synthesis is to bridge the gap between human and machine communication, making our interactions with technology feel seamless, intuitive, and fundamentally more human.
Understanding voice synthesis isn't just for tech enthusiasts anymore. As this technology weaves itself deeper into our daily routines, its importance is skyrocketing. It's making digital content accessible for people with visual impairments, powering the next wave of interactive customer service, and creating entirely new forms of entertainment.
This isn’t some far-off concept from a movie; it’s a practical tool that developers and businesses are using right now to build better products and experiences. Consider this: there are already more than 4.2 billion digital voice assistants being used worldwide, and every single one relies on voice synthesis to speak to us. As we dive into the different methods and applications in this guide, you’ll see just how this once-futuristic idea has become a core part of our world.
To really get a feel for the incredibly natural AI voices we have now, it helps to take a trip back to their humble, often clunky, beginnings. Long before anyone even imagined a computer, inventors were already chasing the dream of making a machine that could talk. This wasn't a quest of software or algorithms—it was a hands-on battle with mechanics, acoustics, and raw ingenuity.
These early pioneers were literally building a voice from the ground up. They used bellows to act as lungs, reeds to vibrate like vocal cords, and custom-shaped tubes to mimic the mouth and throat. The whole idea was to physically assemble a device that could speak by forcing air through a series of mechanical parts.
It was a massive undertaking, but it laid the conceptual foundation for everything that came next.
The dream of a talking machine is an old one, but the first real breakthrough didn't happen until the late 18th century. Voice synthesis, the artificial production of human speech, has come a long way since those first experiments.
The first widely recognized mechanical speech synthesizer was built by Wolfgang von Kempelen back in 1791. It was a wild, bellows-operated contraption that could produce vowels and some consonants by physically imitating the human vocal tract. It was basic, for sure, but it proved that synthesizing speech was even possible, setting the stage for future innovators. If you're curious, you can explore a detailed timeline of this evolution and see how these early ideas led to the tech we use today.
This era was all about physical craftsmanship and a surprisingly deep understanding of human anatomy. Every machine was a unique, hand-built device, painstakingly designed to produce just a few sounds or simple words.
The next giant leap forward came with the dawn of electronics. The focus shifted from mechanical bellows and pipes to circuits, vacuum tubes, and electrical signals. This move gave engineers a level of control and consistency that was simply out of reach with purely mechanical gadgets.
In 1939, Bell Labs showed off the VODER (Voice Operation Demonstrator), the first device to synthesize speech entirely electronically. Designed by Homer Dudley, it was a beast of a machine that needed a trained operator to "play" it with keys and pedals, almost like a strange organ, to create phrases.
The VODER was a hit with the public, demonstrating for the first time that a machine could produce continuous, understandable speech just with electronics. It was no longer just a quirky science project; it was a glimpse into real technological potential.
This was the moment the mechanical era truly ended and the digital frontier began. The principles of manipulating frequencies and tones with electricity, first proven by the VODER, became the bedrock for all modern voice synthesis. From these room-sized machines to the slick AI in our pockets, the fundamental goal has never changed: to give technology a voice that sounds just like us.
Ever wonder how a machine takes a simple line of text and turns it into a voice that sounds convincingly human? It’s not magic, but it is a fascinating process that blends linguistics with some seriously smart technology. The whole journey starts with breaking down the written word into something a computer can actually work with.
This first step is called text preprocessing. The AI scans the text to clean it up and make sense of it. It expands abbreviations ("St." becomes "Saint"), converts numbers to words ("1984" becomes "nineteen eighty-four"), and pays close attention to punctuation to figure out where the natural pauses and inflection points should be. It's a lot like an actor marking up a script, noting where to breathe and which words to punch for emphasis.
Once the text is understood, the real work begins: creating the sound. The methods for doing this have evolved in some incredible ways, moving from clunky, robotic techniques to sophisticated AI that generates a voice from scratch.
This graphic shows just how far we've come, tracing the path from early mechanical attempts to the foundational electronic methods that paved the way for the AI voices we hear today.
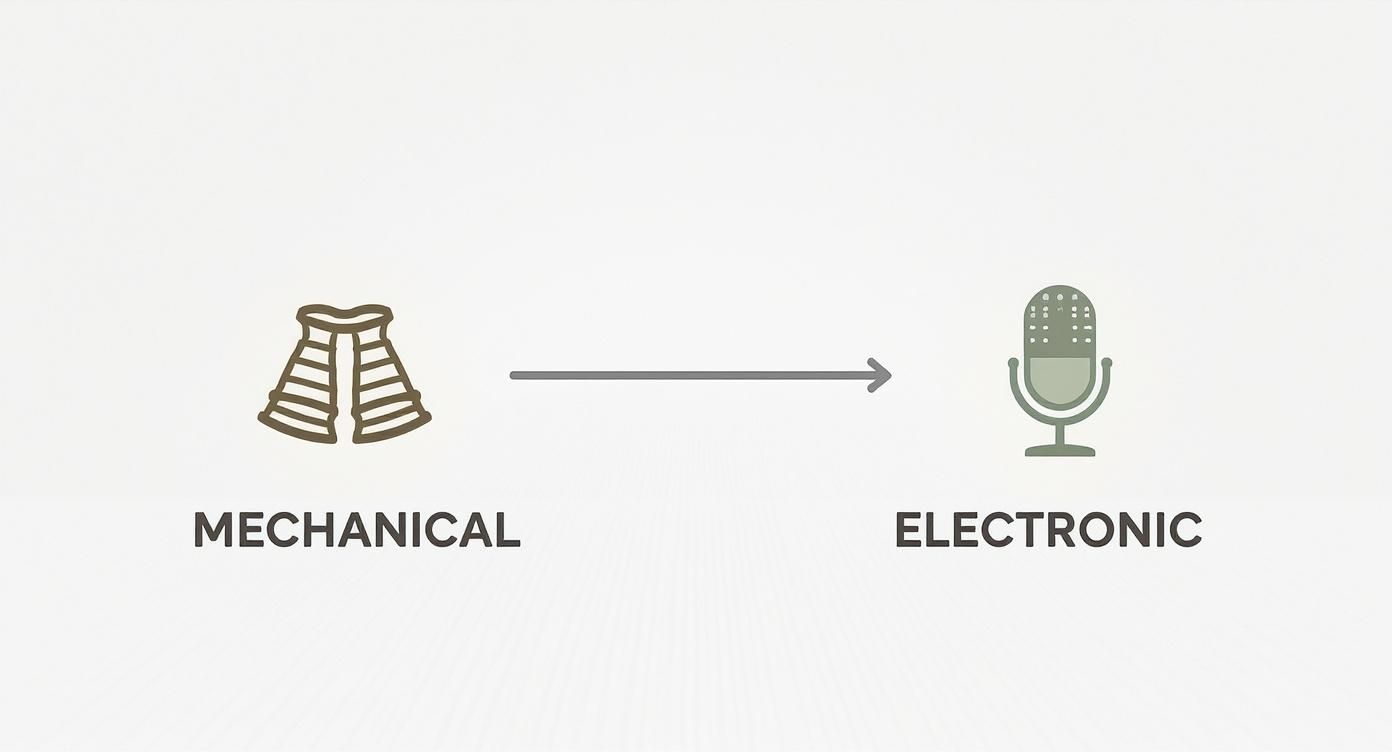
You can see the leap from physical contraptions trying to mimic the vocal tract to electronic systems that gave us direct control over sound waves—a critical step toward the digital speech we now take for granted.
One of the earliest digital approaches was concatenative synthesis. Picture a massive digital library filled with tiny audio clips—individual sounds, syllables, and words—all recorded by one person. To create a sentence, the system would find the audio snippets it needed and stitch them together in the right order.
This "cut-and-paste" method can produce very clear speech for simple, predictable phrases (think of a GPS calmly telling you to "Turn left"). The problem is, it often falls short with more complex sentences. The transitions between the audio snippets can sound choppy or unnatural because the pitch and tone don't always match up perfectly. It's like trying to write a letter by cutting out words from different magazines; you can get the message across, but it’s never going to sound smooth.
The real game-changer has been Neural Text-to-Speech (Neural TTS). Instead of just piecing together pre-recorded audio, neural TTS uses deep learning models to generate brand new, raw audio waveforms from the ground up.
These AI models are trained on massive datasets, often containing thousands of hours of human speech. By listening to all that data, the neural network learns the incredibly complex patterns of how we talk—not just pronunciation, but also the rhythm, intonation, and subtle emotions that make a voice sound human.
Neural TTS doesn’t just mimic speech; it learns to predict what a human would sound like when reading a specific piece of text. That predictive power is the secret sauce behind voices that are often impossible to distinguish from a real person.
This modern approach has some huge advantages:
These advanced capabilities are what power the most realistic virtual assistants, audiobook narrators, and digital avatars in the world today. For instance, brands and creators can now develop a unique online persona by using tools to create AI-powered content that sounds like you. The process has become so refined that the final audio captures the tiny details that make each of our voices unique, signaling a whole new era for voice synthesis.
Chances are, you interact with voice synthesis technology multiple times a day without even realizing it. It's the calm voice guiding you through traffic with your GPS, the automated assistant on a customer service call, or the narrator bringing an audiobook to life on your commute. Voice synthesis has quietly woven itself into the fabric of our daily routines.
This isn't just about convenience. It marks a fundamental change in how we engage with our devices. We're moving beyond keyboards and screens, embracing a more natural, hands-free way of interacting. We can just talk to technology now, which has made it more intuitive and accessible for everyone.
The market numbers back this up. The global text-to-speech (TTS) market was valued at around $3.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to balloon to $8.5 billion by 2027. In 2023, there were already over 4.2 billion digital voice assistants in use across the globe. It’s clear this technology is deeply integrated into our lives. You can discover more insights about the growth of synthetic voice technology to get a better sense of its scale.
One of the most meaningful roles of voice synthesis is in making the digital world accessible to everyone. For millions of people with visual impairments, this technology isn't just a helpful tool—it's a lifeline.
Screen readers are a perfect example. They use TTS to read aloud everything on a screen, from website text and emails to app buttons and system notifications. This gives users who are blind or have low vision the freedom to navigate computers and smartphones on their own.
Businesses have also jumped on board, using voice synthesis to handle customer interactions far more effectively. Those old, clunky, and often frustrating automated phone systems are finally being replaced by smarter, more natural-sounding AI agents.
Modern Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems now use sophisticated TTS to give you clear, dynamic information. They can read your account balance, confirm an appointment, or even field complex questions, all without making you wait for a human agent. This frees up support teams to tackle the tricky problems that actually require a human touch.
By automating routine questions with natural-sounding AI voices, companies can provide 24/7 support, slash wait times, and ensure every customer gets a consistently professional experience.
The creative world is also being reshaped by voice synthesis. Podcasters, video game designers, and other creators are finding all sorts of clever ways to use AI voices.
The applications of voice synthesis are all around us, from helping someone read an email to guiding you through rush-hour traffic. It’s making our world more connected, efficient, and accessible every day.
Now, let's take a look at how these applications play out across different sectors. The technology's flexibility allows it to be adapted for very specific needs, whether it's enhancing safety in a car or making education more engaging.
A comparative look at how different sectors leverage voice synthesis technology to improve efficiency, accessibility, and user experience.
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Reading patient records and medical texts aloud for visually impaired practitioners. | Improved accessibility and accuracy in critical environments. |
| Automotive | In-car navigation systems and hands-free voice commands for infotainment. | Increased driver safety and convenience. |
| Education | E-learning modules with voice-over instruction and reading aids for students. | More engaging and accessible learning for diverse needs. |
| Finance | Automated customer service for balance inquiries and fraud alerts. | 24/7 support and operational efficiency. |
| Retail | In-store announcements and personalized customer service bots. | Enhanced shopping experience and streamlined operations. |
| Telecommunications | Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems for call routing and account management. | Reduced wait times and improved call center productivity. |
As you can see, the core technology is the same, but its impact is felt differently depending on the industry. It's a powerful reminder of just how versatile voice synthesis has become.
As AI voices become practically indistinguishable from human ones, the conversation around voice synthesis shifts from a technical marvel to a pressing ethical dilemma. This technology, especially voice cloning, forces us to ask some tough questions about identity, consent, and how to prevent misuse. The power to perfectly replicate someone's voice from just a few seconds of audio is, without a doubt, a double-edged sword.
On the one hand, the potential for good is genuinely moving. Voice cloning can restore a fundamental part of someone's identity by giving a voice back to those who've lost theirs to illness or injury. Think about someone with a degenerative disease who can continue speaking to their loved ones in their own voice, long after their physical ability is gone.
But with that power comes serious risk. In the wrong hands, cloned voices are the perfect tool for deepfake scams, spreading believable misinformation, or creating fraudulent audio that's nearly impossible to disprove. It all comes down to finding that tricky balance between pushing innovation forward and ensuring it’s done responsibly.
The entire ethical debate really hinges on consent. Whose voice is it, anyway? When an AI can learn and perfectly mimic your voice, you absolutely must have the final say on how that digital version of you is used. The best, most reputable platforms get this, and they're building strict consent verification right into their workflows.
The problem is, the internet is a big place. A bad actor could easily grab a voice sample from a public YouTube video, a podcast, or a social media post. This opens up a legal and ethical can of worms that our current laws are only just beginning to grapple with.
The guiding principle here is simple: A person's voice is part of their identity. It should never be replicated or used without their clear, informed permission.
To get this right, we need a solid framework that covers a few key areas:
One of the most clear and present dangers of voice synthesis is the rise of audio deepfakes. These are incredibly realistic—but completely fake—audio clips that can put words in anyone's mouth. The potential for damage here is huge, from targeted personal harassment all the way up to major societal disruption.
Just think about the fallout. A fake audio clip of a CEO admitting to fraud could tank a company's stock in minutes. A fabricated recording of a world leader declaring war could spark international panic or sway an election. These aren't just hypotheticals anymore; the technology to pull this off is already in the wild.
The good news is that tech companies and researchers are fighting back by developing sophisticated detection tools. These systems are trained to listen for the tiny, almost imperceptible digital fingerprints that AI models often leave behind, helping to flag a recording as synthetic. It's a constant cat-and-mouse game, with the synthesis models getting better and the detection tools racing to keep up. Building a responsible ecosystem around what is voice synthesis means tackling this from all angles—with better technology, smarter policies, and a more informed public.
Knowing how the tech works is one thing, but actually putting it into practice is the real next step. Thanks to a whole host of Text-to-Speech (TTS) APIs, bringing AI voices into your app, product, or content workflow is easier than ever. These tools do all the heavy lifting on the backend, letting you focus on creating a great experience for your users.
But let's be clear: not all voice synthesis services are built the same. The best choice for you depends entirely on what you're trying to accomplish. If you're building a real-time chatbot, for example, low latency is everything. On the other hand, someone producing an audiobook will care far more about emotional nuance and natural delivery.
When you start digging into the options, you have to look past just the sound of the voice. A great first step is to explore some of the top AI voice generators on the market to get a feel for what’s out there. As you compare them, keep these critical factors in mind—they'll make or break your project's success and budget.
Pricing for TTS APIs is all over the map, so it’s crucial to understand the different models to avoid sticker shock down the road. Most services charge you based on how much text you convert, usually measured by the character or the number of requests.
Don't just look at the per-character price. Consider the value you get, including the quality of the voices, the reliability of the service, and the level of developer support provided. An ultra-cheap option might cost you more in the long run if it delivers a poor user experience.
You’ll typically run into one of these three pricing structures:
Ultimately, picking the right API is a balancing act between quality, features, and cost. If you carefully weigh these factors against your project’s specific needs, you’ll find a tool that can bring your ideas to life with a voice that truly connects with your audience.
We’ve covered a lot of ground, from the clunky beginnings of talking machines to the sophisticated AI voices we interact with daily. As we wrap up, let's tackle a few of the most common questions people have.
It’s easy to mix these two up, but they're essentially opposite sides of the same conversation.
Think of it this way: voice synthesis is how a machine talks. It turns text into spoken words. Your GPS reading out turn-by-turn directions? That's voice synthesis in action.
Speech recognition, on the other hand, is how a machine listens. It captures your spoken words and converts them back into text. When you dictate a text message to your phone, you're using speech recognition.
Your favorite smart assistant is the perfect example of these two working together. It listens to your command (speech recognition) and then talks back with an answer (voice synthesis).
Honestly? The best ones are shockingly good. We've come a long, long way from the robotic monotones of the past.
Modern AI voices, especially those built on neural networks, can be virtually indistinguishable from a human speaker, particularly in shorter clips. They can mimic the subtle inflections, natural pauses, and unique cadence that make human speech feel alive. The quality still depends on the underlying tech and the data it was trained on, but the top-tier systems are truly impressive.
This is where things get tricky, as the law is still catching up to the technology. The short answer is: cloning someone's voice without their explicit consent is a major legal and ethical minefield. Using it for commercial purposes, impersonation, or fraud is almost certainly illegal.
Any reputable voice synthesis platform will demand clear, verifiable permission from the voice donor before creating a clone. If you're a developer or business, you absolutely must put ethics first and always get consent.
SSML stands for Speech Synthesis Markup Language. The easiest way to think of it is as a set of stage directions for your AI voice. By adding simple tags to your text, you can tell the AI exactly how to say something.
This gives you an incredible amount of control. You can use SSML to adjust pronunciation, change the pitch, speed up or slow down the speaking rate, or add emphasis to certain words. It's the key to turning a flat, uniform reading into a dynamic and expressive performance.
Ready to bring lifelike voices to your own projects? Lemonfox.ai provides a simple and affordable Text-to-Speech API that puts premium voice technology within reach for any application. Generate high-quality, human-like audio effortlessly and at a fraction of the cost of other services. Start building with our voice synthesis API today!